国内外学者对用户体验进行了大量理论和实践研究,提出了许多用户体验模型,本书着重介绍Hassenzah提出的用户体验要素模型(如图7.5所示),该模型假定用户体验是在特定情境中对产品内容、功能、呈现及交互的体验,通过感知产品的实用性和享受性特征进而产生用户体验结果。他认为实用性和用户完成任务的需求相关,主要指有用性和易用性;而享受性主要和用户自身相关,如有趣性、创新性等。
该模型被许多学者运用于用户体验理论拓展与实践应用中。部分学者对其用户体验要素理论进行拓展,如增加了美学和综合质量等用户体验要素。Hassenzahl[84]本人在随后的研究中,进一步探究了用户所感知的美学、综合质量和实用性、享受性之间的关系。Schaik和Ling[85]构建了基于实用性、享受性、美学及综合质量的用户体验模型,探讨了用户使用网站之前和之后的用户感知实用性、享受性对感知美学、综合质量的影响。De Angeli[86]、Tuch[87]等通过实证分析探究了用户对网站交互界面的感知美学和感知实用性之间的关系,并且对用户使用网站前后的评价分别进行了研究。
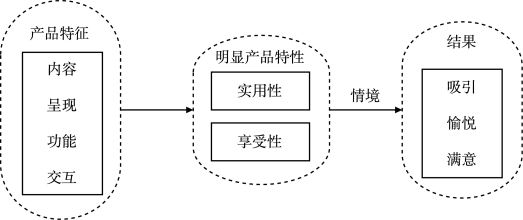
图7.5 Hassenzah用户体验要素图
也有学者将Hassenzah用户体验要素模型运用于各种人机交互的实际应用及评价,如推荐系统、e-learning等。Zaharias和Poylymenakou[88]从用户认知和情感两个方面对e-learning应用系统的实用性进行评价,Ozkan和Koseler[89]等人从用户维度和系统维度分别对e-learning系统质量进行评价,他们都通过问卷调查进行实证分析。Xiao[90]、Ozok[91]和Knijnenburg[92]等将用户体验要素模型运用于推荐系统用户体验研究,他们通过调查发现用户感知推荐系统的质量(如交互性、界面)对用户态度和行为会产生影响,并且Ozok等[93]还设计出一套推荐系统实用性的评价指标。
综上所述,Hassenzah用户体验模型在人机交互理论与实践方面都获得了广泛运用。本书将人机交互系统用户体验的影响因素划分为系统维度及感知维度。系统维度涉及界面设计、内容、交互等因素,感知维度涉及用户感知有用性、感知易用性及感知享受性等因素。
本书认为Hassenzahl的模型适用于本研究是基于两个原因。首先,Hassenzahl的模型侧重于社交问答平台研究中普遍存在的产品交互的用户体验影响因素。在社交问答平台中,信息贡献是基于人机交互和人人交互基础之上的,且用户间交互贯穿整个体验过程。其次,该模型还被广泛应用于人机交互领域和人人交互领域。
(1)社交问答平台用户体验影响因素假设与模型
由上文可知,人机交互系统用户体验的影响因素可划分为系统特征维度和技术感知维度。对于社交问答平台用户体验而言,Park等[94]通过调查研究发现,答案质量及交互性对问答平台用户体验满意度会产生影响。Thong等[95]发现系统界面设计质量对数字图书馆的使用具有显著影响,且其常被列为用户不使用电子信息检索系统的主要因素[96]。基于现有研究,本书将系统特征维度设定为三个因素,即界面设计、社交问答交互及答案质量。而对于技术感知维度,本书在Hassenzahl提出的感知实用性和感知享受性的基础上,基于Thong等人的研究结果,将实用性进一步划分为感知易用性、感知有用性和感知享受性。因此,社交问答平台用户通过对界面设计合理性与答案质量、问答交互有效性的感知过程,产生了不同的体验结果。因此,本书假设模型如图7.6所示。
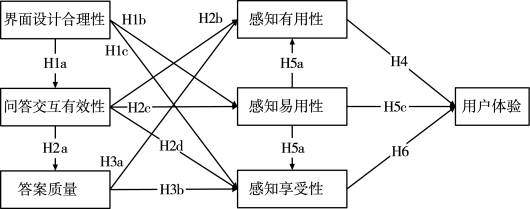
图7.6 社交问答平台用户体验影响因素模型
Mahlke和Thuring[97]提出的用户体验模型表明,诸如功能、界面设计等系统特征会产生交互影响并确定主要特征。技术接受模型(TAM)[98]指出,外部系统变量通过感知易用性和感知有用性间接作用于用户使用意图。Davis等[99]进一步提出系统变量作用用户使用意向的过程受到感知享受性的调节。Thong等[100]在对数字图书馆用户接受度研究中指出,导航、屏幕设计等界面特性会对用户感知易用性产生影响,良好的界面设计能够帮助用户更容易地使用系统。赵慧文[101]在网络用户体验及交互设计中指出,界面是用户与用户或产品互动的窗口,合理清晰的界面设计,有利于增强用户享受性,良好的用户体验需要设计者以符合用户感觉认知和情感接受为导向,对界面元素进行科学合理组织。因此,本书提出如下假设:
H1a:社交问答平台界面设计合理性与问答交互有效性成正相关;
H1b:社交问答平台界面设计合理性与用户感知易用性成正相关;
H1c'社交问答平台界面设计合理性与用户感知享受性成正相关。
Myers[102]在协作式学习研究中指出,通过学习者之间的互动交流,他们将自身隐性知识转化为显性知识供群体共享,即有效的交互能够增强知识外显化程度,提升知识质量。知识的共享与交流也使得个人知识转化为社会知识[103]。Hassenzahl[104]在用户与产品交互研究中指出,交互作为产品特征之一会影响用户感知产品实用性和享受性。Mahlke等[105]在用户体验要素研究中指出,交互特征作为交互系统固有特征会影响用户对系统的技术性感知(如感知易用性、感知有用性)和非技术性感知(视觉美感、视觉享受)。技术接受模型提出用户的感知易用性与感知有用性相关,用户对信息系统交互过程的感知易用性会影响用户使用意图。因此,本书提出如下假设:
H2a:社交问答平台问答交互有效性与答案质量成正相关;
H2b:社交问答平台问答交互有效性与用户感知有用性成正相关;
H2c:社交问答平台问答交互有效性与用户感知易用性成正相关;
H2d:社交问答平台问答交互有效性与用户感知享受性成正相关。
Yu[106]研究发现社交问答平台用户对其获取知识的感知有用性越强烈,则用户整体满意度越高,即知识感知有用性能够使用户产生积极用户体验。Park等[107]发现,问答质量是用户选择问答平台的最重要因素,相比搜索引擎的搜索结果而言,社交问答平台的问答结果对解决问题更有用。Hassenzahl[108]研究用户与产品交互影响模型时提到,良好的产品内容体验能够使用户产生享受性感知,也就是说高质量的答案不仅能够提高用户知识水平和答案自信度,还能提高用户的享受性感知。因此,本书提出如下假设:
H3a:社交问答平台答案质量与用户感知有用性成正相关;
H3b:社交问答平台答案质量与用户感知享受性成正相关。
Davis等[109]在系统用户接受度研究中指出,感知易用性会影响感知有用性和感知享受性。Hassenzahl等[110]在对软件系统用户体验研究中指出,人体工学质量(EQ)和享受性质量(HQ)会影响用户对系统的评价及用户体验,其中EQ主要指系统易用性和有用性,HQ主要指创意、有趣性。Mahlke[111]在网站用户体验影响因素研究中指出,网站用户体验的影响因素包括感知有用性、感知易用性、感知享受性及审美感知。Schaik[112]在构建网站用户体验模型时指出,用户对网站的综合质量的评价受到用户对网站实用性和享受性的感知影响。Park、Han、Kim、Oh、Moon[113]在对用户体验要素的研究中指出,用户体验涉及用户价值、总体用户体验、感知实用性和用户情感四个方面,而总体用户体验则受到其他几方面的影响。据此,本书提出如下假设:
H4:社交问答平台用户感知有用性与用户体验成正相关;
H5a:社交问答平台用户感知易用性与用户感知有用性成正相关;
H5b:社交问答平台用户感知易用性与用户感知享受性成正相关;
H5c:社交问答平台用户感知易用性与用户体验成正相关;
H6:社交问答平台用户感知享受性与用户体验成正相关。
(2)模型验证与结论
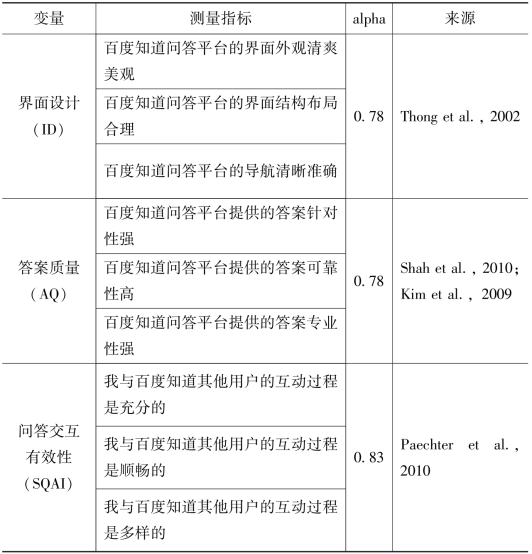
基于上述研究模型,本书设计了相应的调查问卷,并选取百度知道这一中国最大的社交问答平台作为此次调查的对象。社交问答平台有特殊性,因此本书的测量指标在借鉴已有中外文文献的基础上进行修改,并根据预调查的结果进行了调整。最终该研究模型中共有7个潜变量,每个潜变量下有2~3个测量变量,问卷内容及来源如表7.13所示。该问卷题项采用李克特5级量表(1~5分别代表“完全不同意”到“完全同意”)进行测试。
表7.13 量表指标、alpha值及文献来源
续表
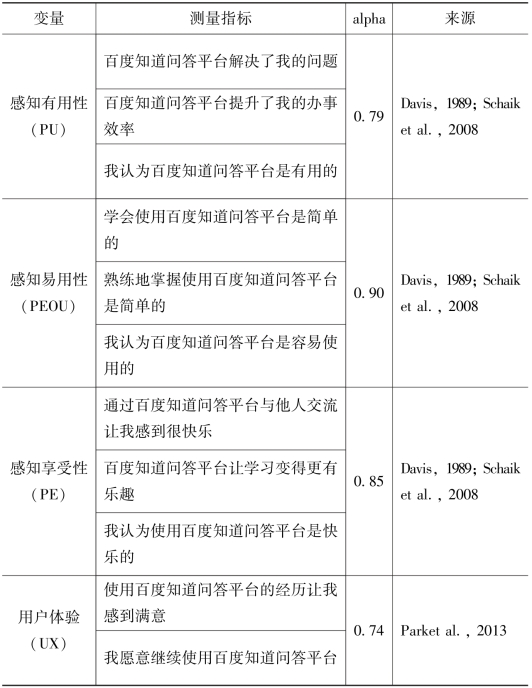
界面设计测量项目改编自Thong、Hong和Tam[114],考虑到测度全面性,本书添加屏幕外观这一测量项。由于当前并没有有关社交问答平台互动性的测量量表,本书以Paechter等[115]的方法为基础修正并开发了交互性测量项,其中本书用同级学生间的交互体验代替在线学习系统学生间的互动。社交问答互动有效性的三个测量项来自Paechter等[116]的研究。涉及答案质量的三个测量项采用Shah[117]和Kim[118]等的现有量表。有关答案质量的测量项,本书总结了以往关于用户答案评价标准度量的研究结果。测量感知有用性及感知易用性的测量项分别源自Davis[119]与Schaik等[120]的已有研究。本书结合社交问答平台的主要特点(如信息共享和互动导向)进行测量项目的构建,通过总结Davis等[121]和Schaik等[122]对社交问答网站内容的研究成果,来构建感知享受性的测量问项,测度用户体验的两个问项则来源于Park等[123]的研究成果,因为其反映了用户体验的两个方面,即情感和公开行为。
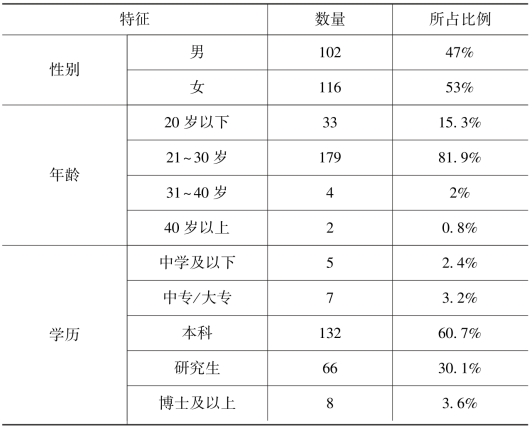
此次问卷调查在2026年7月23日到2026年8月5日进行,并通过委托专业的在线问卷调查网站问卷星收集数据。百度知道包含了生活、情感、体育等14个大类,为了保证样本的随机分布,本次调查对在不同类提问的用户共发出了2 100个调查请求,每个大类各150份,共回收有效问卷218份,占比约为10.4%。样本分布特征如表7.14所示,被调查者中男性和女性比例相差不大,且年龄集中在21~30岁,拥有本科以上学历人数近75%,超过60%参与者使用百度知道的时间超过3年。
表7.14 样本特征分布
续表

本研究使用结构方程模型分析软件LISREL8.7和SPSS20.0对样本数据进行信度、效度及假设检验。并采用Andersen和Gerbing[124]的两步骤法分析测量模型和结构模型。
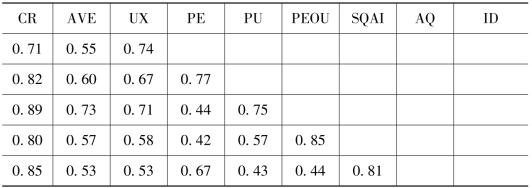
①测量模型。本书采用Cronbach'sα系数和组合信度来评测问卷题项。当Cronbach'sα系数大于0.7,并且组合信度大于最小临界值0.7时,表明测量结果具有较好的信度[125]。如表7.13和表7.15所示,所有因子的Cronbach'sα系数和组合信度都大于0.7,并且组合信度CR值大于最小临界值0.7,因此本书的测量指标具有较好的信度。
表7.15 信度与效度
续表
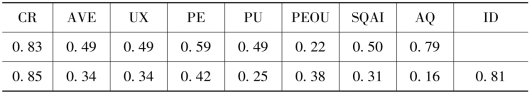
注:CR=组合信度,AVE=平均提取方差值,UX=用户体验,PE=感知享受性,PU=感知有用性,PEOU=感知易用性,SQAI=社交问答平台互动有效性,AQ=答案质量,ID=界面设计。
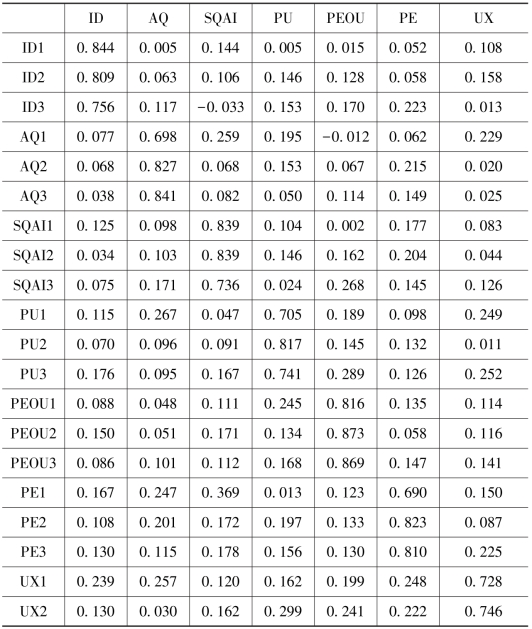
效度包括收敛效度和区别效度。收敛效度主要是通过因子载荷和平均变异抽取量来进行评测,因子载荷反映了测量指标对潜变量的相对重要性,平均变异抽取量则反映了测量指标相对于测量误差而言被潜变量构念解释的变异量,两者均应大于0.5[126] [127]。由表7.15、表7.16可知,各因子载荷和平均变量值均大于0.5,这表明了该测量指标具有较好的收敛效度。由表7.15可知,各潜变量AVE值的平方根均大于该潜变量与其他潜变量之间的标准化相关系数,表明该测量指标具有较好的区别效度。对于存在的个别变量之间的相关系数高于0.6的情况(如UX和PU的相关系数为0.71),为了消除高相关性影响,我们检查了方差膨胀因子(VIF),VIF用于自变量间的多重共线性诊断,VIF临界值为3[128],VIF越大,则共线性越严重。经检查发现,每个自变量的VIF都小于3,表明各变量相关性在可接受范围之内。鉴于常用方法的局限性,本研究在单因素检验[129]后探索性地进行了Harman's因子分析。根据结果可知常用方法并不会严重影响内部效度。
表7.16 负荷与交叉负荷
②结构模型。表7.16和表7.17为总体结构模型分析结果。由图7.7可以看出,除H2b、H5b和H5c之外,其余11个假设均获得了样本数据的支持。首先来看社交问答平台用户体验的三个直接影响因素。假设与预期一致,感知有用性和感知享受性对用户体验有显著正向影响,因此H4(β=0.45,t=4.8)和H6(β=0.41,t=5.01)得到支持。感知易用性与感知有用性正向相关,故H5a(β=0.47,t=5.82)成立。
表7.17 假设检验结果(β=regression weight,:P<0.001)
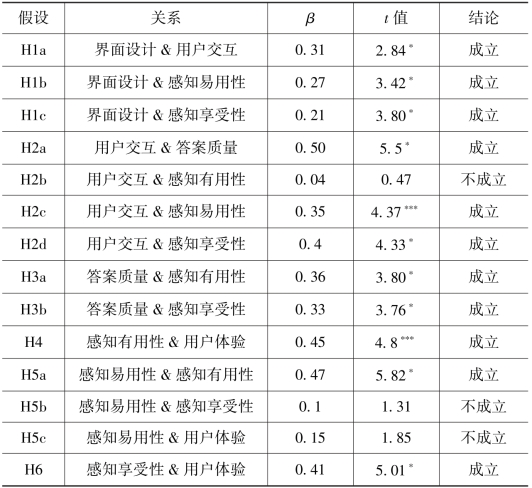
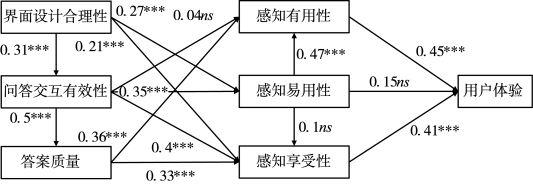
图7.7 研究模型路径分析结果(P<0.001;ns表示不显著)
用户体验的三个间接外部影响因素中,界面设计合理性对问答交互有效性、用户感知易用性和感知享受性有显著正向影响,因此H1a(β=0.31,t=2.84)、H1b(β=0.27,t=3.42)和H1c(β=0.21,t=3.80)得到支持。问答交互有效性对答案质量、感知易用性和感知享受性有显著正向影响,因而H2a(β=0.5,t=5.5)、H2c(β=0.35,t=4.37)和H2d(β=0.4,t=4.33)成立。但是问答交互有效性对感知有用性的影响不显著,假设H2b(β=0.04,t=0.47)不成立。答案质量对感知有用性和感知享受性有显著正向影响,H3a(β=0.36,t=3.80)和H3b(β=0.33,t=3.76)成立。
本研究在前人对社交问答平台用户体验相关研究基础上,构建了社交问答平台用户体验影响因素模型,并以百度知道为例进行了实证研究,通过以上数据分析,本书得出以下研究结论,同时对问答平台管理者提出几点建议。
①结果显示界面设计对问答交互性具有显著影响。换言之,界面设计对于促进用户与用户、用户与系统之间问答交互有效性有重要影响,整洁、美观的界面设计有利于用户间的交流沟通。这一发现补充了以往关于界面设计与人机交互关系研究的不足。因此,本书认为业界应该重视界面设计的有效性,界面设计通过问答交互性间接影响感知易用性和感知享受性。本研究发现响应了Thong等[130]和Davis[131]的研究成果,用户更愿意使用布局清晰、设计美观的系统。
②问答交互有效性对用户感知易用性、感知享受性及答案质量的正面影响显著,这与Mahlke等[132]、Myers[133]和Knijnenburg[134]的研究结果相一致。问答交互有效性对用户感知有用性没有显著影响,这与Hassenzahl[135]和Mahlke等[136]研究结果有所差异。我们认为这种差异是由于研究对象不同所导致的,前人的研究大多是针对人机交互系统,而本次研究的对象是交互式知识问答社区,人人交互才是重点。张兴刚和袁毅[137]通过对国内5个社交问答平台的比较研究发现,在百度知道中,平均每个问题用户可以收到超过4个有用的答案。这意味着大部分提问者通过回答者一次性回答获取了答案,回答者通过与提问者互动来修改完善答案的比例很低。因此,问答平台用户的问答交互积极性并不直接影响用户的感知有用性。此外,我们还发现交互有效性通过感知易用性的中介作用间接影响感知有用性,然而,交互有效性对感知有用性并无直接影响。
③本研究发现,答案质量对社交问答平台用户感知有用性和感知享受性有显著正面影响,这与Kim等[138]和Park等[139]的研究结果一致。这说明评价答案质量的好坏,不仅要看其内容价值和效用,还需要看它的社会情感和认知价值,即高质量的答案不仅能够及时有效地解决用户难题,还能提升用户知识水平,增强自信和满足感。因此,社交问答平台管理者应该建立严格的审核机制,剔除低质量答案,整合高质量答案。此外,问答平台可以与各领域知名单位合作,共享资源,扩充专家团队,提升答案专业性。
④感知有用性和感知享受性对社交问答平台用户体验有显著正面影响。这与以往研究结果相符,说明社交问答平台能否帮助用户解决实际难题是其作为知识问答社区的核心价值所在,也是用户获取良好信息体验的关键。感知享受性主要表现为激励和认同,运用于问答平台,即指用户通过知识共享创新获取社区其他成员的认同,物质和精神激励又进一步刺激用户不断创新、挖掘内在知识,提升用户享受性体验。因此,社交问答平台管理者需要加强知识组织分类的能力,按照用户个性化需求进行知识推荐服务,而不是提供单一大众化的知识内容。另外,平台可以在保证答案质量的基础上丰富知识共享的形式和内容,并增设相关娱乐板块,让用户在获取知识的同时享受快乐。
⑤感知易用性对感知享受性和用户体验没有显著影响。究其原因,本问卷被调查者学历为本科及以上的占94%,并且同时使用其他问答平台的用户占84%,如知乎、YaHoo!Answer等。另外根据艾瑞[140]调查结果显示,绝大多数国内的问答平台功能相似、差异性较小。由此可见,百度知道用户大多也同时使用其他问答平台,各平台操作流程大同小异,用户对百度知道平台感知易用性较弱,对其满意度及继续使用不会造成明显影响。因此,用户可能不会在感知易用性的基础上评价用户体验。由于各问答平台运作的相似性,感知有用性和感知享受性成为用户评价系统体验的决定因素。感知易用性可以通过感知有用性的中介作用间接对用户体验产生影响,这一发现与Davis[141]和Xiao等[142]的研究结果一致。
以上研究结论在一定程度上说明了社交问答平台用户体验影响因素及其影响程度,为提升百度知道乃至其他社交问答平台用户体验提供了一定的参考。本研究对社交问答平台的理论研究及问题导向、社交导向的用户体验研究都具有重要影响,且当前有学者关注社交问答平台的用户体验研究。本研究一方面通过探索系统特征和用户技术感知来识别用户体验的影响因素;另一方面,界面设计、用户交互和回答质量有效促进了用户感知有用性、感知易用性和感知享受性,也为管理者提供了有效的实践指导。因此,应注重界面设计的改善以促进社交问答平台的交互性。
本书在研究中还存在许多不足。首先,感知有用性、感知易用性、感知享受性及用户体验分别只有47%、26%、59%和68%的方差得到解释,这说明还有其他因素影响用户感知及体验。其次,本书以百度知道为例进行研究,研究对象较为单一,还有许多问答平台的用户体验没有考虑。这些问题将在接下来的深入研究中逐步改进完善。
社交问答服务作为新一代交互式信息服务的典范,是社交网络与问答平台的完美结合,它的出现为学者们提供了一个新的研究视角。然而,社交问答平台仍处于起步阶段,发展过程中出现了很多问题,如答案质量不高、参与率低,而有关该项服务的用户体验研究较为缺乏。因此,本书以社交问答平台为研究对象,从系统维度和感知维度出发,对平台用户体验的影响因素进行研究。根据研究结果,我们发现问答低质量和低参与率会影响用户感知有用性和感知享受性,从而降低用户对服务的满意度。本书研究成果不仅使我们对社交问答平台用户体验有了更好的认识,同时也为运营商改善问答平台服务提供了参考依据。
除了本研究已确定的因素外,未来的研究还可以考虑答案来源及用户的美学感知等因素对用户体验的影响。随着社交问答平台服务的发展及数量的增加,有效组织海量问答资源以便用户及时获取答案显得十分重要。此外,关于用户界面的美学研究也是用户体验研究感兴趣的主题,例如,美学对信任和可信度的影响研究。
【注释】
[1]Shah C,Oh S,Oh J S.Research agenda for social Q&A[J].Library&Information Science Research,2009,31(4):205-209.
[2]Shah C,Oh S,Oh J S.Research agenda for social Q&A[J].Library&Information Science Research,2009,31(4):205-209.
[3]黄梦婷,张鹏翼.社会化问答社区的协作方式与效果研究:以知乎为例[J].图书情报工作,2015,59(12):85-92.
[4]Chen X,Deng S.Influencing factors of answer adoption in social Q&A communities from users’perspective:taking Zhihu as an example[J/OL].Chinese Journal of Library and Information Science,2014,7(3):81-95[2015-11-15].http://ir.las.ac.cn/handle/12502/7568.
[5]刘高勇,邓胜利.社交问答服务的演变与发展研究[J].图书馆论坛,2013,33(1):17-21.
[6]贾佳,宋恩梅,苏环.社会化问答平台的答案质量评估——以知乎、百度知道为例[J].信息资源管理学报,2013(2):19-28.
[7]Savolainen R.Providing informational support in an online discussion group and a Q&A site:the case of travel planning[J].Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology,2015,66(3):450-461.
[8]Cohen J.A coefficient of agreement for nominal scale[J].Educ Psychol Meas,1960,20(1):37-46.
[9]Lindlof T R,Taylor B C.Qualitative communication research methods[M].Sage,2010.
[10]郑全全,赵立,谢天.社会心理学研究方法[M].北京:北京师范大学出版社,2010.
[11]李小宇.中国互联网内容监管机制研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2014.
[12]黄晓斌,粱辰.质性分析工具在情报学中的应用[J].图书情报知识,2014(5):4-16.
[13]刘鲁川,蒋晓阳.社区公共服务综合信息平台居民使用行为研究[J].中国图书馆学报,2015,41(6):61-72.
[14]Abrahamson J A,Rubin V L.Discourse structure differences in lay and professional health communication[J].Journal of Documentation,2012,68(6):826-851.
[15]Savolainen R.The structure of argument patterns on a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2012,63(12):2536-2548.
[16]Savolainen R.Expressing emotions in information sharing:a study of online discussion about immigration[J/OL].Information Research,2015,20(1):350-364[2015-09-28].http://InformationR.net/ir/201/pape-r662.html.
[17]林臻,熊信之.社会化问答网站的传播特点及发展策略[J].青年记者,2012(33):83-84.
[18]Zhang W,Watts S.Knowledge adoption in online communities of practice[J].ICIS 2003 Proceedings,2003:9.
[19]蒋楠,王鹏程.社会化问答服务中用户需求与信息内容的相关性评价研究——以百度知道为例[J].信息资源管理学报,2012(3):35-45.
[20]Shah C,Pomerantz J.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community QA[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.ACM,2010:411-418.
[21]Zhu Z M,Bernhard D,Gurevych I.A multi-dimensional model for assessing the quality of answers in social Q&A[EB/OL].[2014-04-16].http://tuprints.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de/1940/1/TR_dimension_model.pdf.
[22]Soojung K,Sanghee O.Uses’relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[23]Sussman S W,Siegal W S.Information influence in organizations:an integrated approach to knowledge adoption[J].Information System Research,2003,14(1):47-65.
[24]Davis F D.Perceived usefulness,perceived ease of use and user acceptance of information technology[J].MIS Quarterly,1989,13(3):319-340.
[25]Petty R E,Cacioppo J T.Communication and persuasion:central and peripheral routes to attitude change[M].New York:Springer,1986.
[26]Cheung C M K,Lee M K O,Rabjohn N.the impact of electronic word-ofmouth:the adoption of online opinions in online customer communities[J].Internet Research,2008,18(3):229-247.
[27]Zhang W,Watts S.Knowledge adoption in online communities of practice[J].ICIS 2003 Proceedings,2003:9.
[28]Deng S L,Liu Y,Qi Y.An empirical study on determinants of web based question-answer services adoption[J].Online Information Review,2011,35(5):789-798.
[29]Zhang W,Watts S.Knowledge adoption in online communities of practice[M].ICIS 2003 Proceedings,2003:9[2014-04-16].http://aisel.aisnet.org/icis2003/9/.
[30]Deng S L,Liu Y,Qi Y.An empirical study on determinants of web based question-answer services adoption[J].Online Information Review,2011,35(5):789-798.
[31]Chirag S,Sanghee O,Jung S.Research agenda for social Q&A[J].Library&Information Science Research,2009,31:205-209.
[32]Soojung K,Sanghee O.Uses’relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[33]Zhu Z M,Bernhard D,Gurevych I.A multi-dimensional model for assessing the quality of answers in social Q&A[EB/OL].[2014-08-16].http://tuprints.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de/1940/1/TR_dimension_model.pdf.
[34]Shah C,Pomerantz J.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community Q&A[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.ACM,2010:411-418.
[35]Zhu Z M,Bernhard D,Gurevych I.A multi-dimensional model for assessing the quality of answers in social Q&A[EB/OL].[2014-08-16].http://tuprints.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de/1940/1/TR_dimension_model.pdf.
[36]Shah C,Pomerantz J.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community Q&A[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.ACM,2010:411-418.
[37]Soojung K,Sanghee O.Uses’relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[38]Shah C,Pomerantz J.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community Q&A[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.ACM,2010:411-418.(https://www.daowen.com)
[39]蒋楠,王鹏程.社会化问答服务中用户需求与信息内容的相关性评价研究——以百度知道为例[J].信息资源管理学报,2012(3):35-45.
[40]Jia J,Song E M,Su H.Research on assessment of answer quality in social Q&A platform[J].Journal of Information Resources Management(in Chinese),2013,3(2):19-28.
[41]Chua A Y K,Banerjee S.So fast so good:an analysis of answer quality and answer speed in community question-answering sites[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2013,64(10):2058-2068.
[42]Chua A Y K,Banerjee S.So fast so good:an analysis of answer quality and answer speed in community question-answering sites[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2013,64(10):2058-2068.
[43]贾佳,宋恩梅,苏环.社会化问答平台的答案质量评估:以知乎、百度知道为例[J].信息资源管理学报,2013,3(2):19-28.
[44]Utpal M D,Richard P B,Lisa K P.A social influence model of consumer participation in network-and small-group-based virtual communities[J].International Journal of Research in Marketing,2004,21(3):241-263.
[45]Soojung K,Sanghee O.Uses’relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[46]Utpal M D,Richard P B,Lisa K P.A social influence model of consumer participation in network-and small-group-based virtual communities[J]..International Journal of Research in Marketing,2004,21(3):241-263.
[47]Cao S J,Chen Y J,Yang T.An empirical study on library user satisfaction based on user needs[J].Journal of Library Science in China(in Chinese),2013(5):60-75.
[48]Zhu Z M,Bernhard D,Gurevych I.A multi-dimensional model for assessing the quality of answers in social Q&A[EB/OL].[2014-08-16].http://tuprints.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de/1940/1/TR_dimension_model.pdf.
[49]Utpal M D,Richard P B,Lisa K P.A social influence model of consumer participation in network and small-group-based virtual communities[J].International Journal of Research in Marketing,2004,21(3):241-263.
[50]Shah C,Pomerantz J.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community Q&A[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.ACM,2010:411-418.
[51]Deng S L,Liu Y,Qi Y.An empirical study on determinants of web based question-answer services adoption[J].Online Information Review,2011,35(5):789-798.
[52]Hassenzahl M.The thing and I:understanding the relationship between user and product[C]//M A Blythe,K Overbeeke,A F Monk P C Wright(Eds.).Funology:From Usability to Enjoyment.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Kluwer,2003:31-42.
[53]Stvilia B,Twidale M B,Smith L C,Gasser L.Assessing information quality of a community-based encyclopedia[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Quality.Cambridge,MA,2005:442-454.
[54]Yan Z,Zhou J.A new approach to answerer recommendation in community question answering services[C]//R Baeza-Yates,A P de Vries,H Zaragoza,B B Cambazoglu,V Murdock,R Lempel,F Silvestri(Eds.).Advances in information retrieval.Berlin Heidelberg:Springer,2012:121-132.
[55]Li B,King I.Routing questions to appropriate answerers in community question answering services[C]//Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.New York,NY:ACM,2010:1585-1588.
[56]Guo J,Xu S,Bao S,Yu Y.Tapping on the potential of Q&A community by recommending answer providers[C]//Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.New York,NY:ACM,2008:921-930.
[57]iResearch.The research on knowledge question&answer platforms[EB/OL].[2016-10-20].http://tech.china.com/zh_cn/news/net/domestic/11066127/20100618/15985713.html.
[58]李晨,巢文涵,陈小明,等.中文社区问答中问题答案质量评价和预测[J].计算机科学,2011(6):230-236.
[59]Hart J,Ridley C,Taher F,Sas C,Dix A T K,Jönsson B.Exploring the Facebook experience:a new approach to usability[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction:Building Bridges.New York,NY:ACM,2008:471-474.
[60]刘璇.传播心理学视角下的中国社交网络(SNS)用户心理体验研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2010.
[61]赖茂生,麦晓华.面向使用过程的社交问答网站用户体验研究[C]//第七届和谐人机环境联合学术会议(HHME2011)论文集.北京,2011.
[62]Eric W K See-To,Savvas Papagiannidis,Vincent Cho.User experience on mobile video appreciation:how to engross users and to enhance their enjoyment in watching mobile video clips[J].Technological Forecasting&Social Change.2012,79:1484-1494.
[63]Vyas D,Gerrit C,Van Der V.APEC:a framework for designing experience[EB/OL].[2006-06-11].http://www.infosci.cornell.edu/place/15_DVyas2005.pdf.
[64]杜海.SNS网站的用户体验研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2013.
[65]Paechter M,Maier B,Macher D.Students'expectations of,and experiences in elearning:their relation to learning achievements and course satisfaction[J].Computers&Education,2010,54(1):222-229.
[66]Baird D E,Fisher M.Neomillennial user experience design strategies:utilizing social networking media to support“always on”learning styles[J].Journal of Educational Technology Systems,2005,34(1):5-32.
[67]Kenney B.Liverpool's discovery:a university library applies a new search tool to improve the user experience[J].Library Journal,2011,136(3):24-27.
[68]何小丽.用户体验在搜索引擎营销策略中的作用研究[D].北京:对外经济贸易大学,2007.
[69]裴一蕾,薛万欣,赵宗,等.基于用户体验视角的搜索引擎评价研究[J].情报科学,2013,31(5):94-112.
[70]Oh S.The relationships between motivations and answering strategies:an exploratory review of health answerers'behaviors in Yahoo!Answers[J].Proceedings of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2011,48(1):1-9.
[71]Park J,Jeong D.An empirical study on web based question-answer services[J].Journal of the Korean Society for Information Management,2004,21(3):83-98.
[72]Yu S-L.Toward a new knowledge sharing community:collective intelligence and learningthrough Web-based question-answer services[D].Washington,DC:Georgetown University,2006.
[73]高山.问答型虚拟社区用户满意度影响因素研究[D].安徽:安徽大学,2013.
[74]金晓玲.探讨网上问答社区的可持续发展[D].安徽:中国科学技术大学,2009.
[75]樊彩锋,查先进.互动问答平台用户贡献意愿影响因素实证分析[J].信息资源管理学报,2013(3):30-38.
[76]Shah C,Pomerantz J,Crestani F,Marchand-maillet S,Phane Chen H,Efthimiadis E N.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community Q&A[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.New York,NY:ACM,2010:411-418.
[77]Chua A Y K,Banerjee S.So fast so good:an analysis of answer quality and answer speed in community question answering sites[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2013,64(10):2058-2068.
[78]Zhou Y,Cong G,Cui B,Jensen C S,Yao J.Routing questions to the right users in online communities[C]//Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering.Washington,DC:IEEE Computer Society,2009:700-711.
[79]Kim S,Oh S.Users'relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[80]李晨,巢文涵,陈小明,等.中文社区问答中问题答案质量评价和预测[J].计算机科学,2011(6):230-236.
[81]来社安,蔡中民.基于相似度的问答社区问答质量评价方法[J].计算机应用与软件,2013(2):266-269.
[82]曲明成.问答社区中的问题与答案推荐机制研究与实现[D].浙江:浙江大学,2010.
[83]Hassenzahl M.The thing and I:understanding the relationship between user and product[C]//M A Blythe,K Overbeeke,A F Monk,P C Wright(Eds.).Funology:From Usability to Enjoyment.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Kluwer,2003:31-42.
[84]Hassenzahl M.The interplay of beauty,goodness and usability in interactive products[J].Human-Computer Interaction,2004,19(4):319-349.
[85]Schaik P V,Ling J.Modelling user experience with web sites:usability,hedonic value,beauty and goodness[J].Interacting with Computers,2008,20(3),419-432.
[86]De Angeli A,Sutcliffe A,Hartmann J.Interaction,usability and aesthetics:what influences users'preferences?[C]//Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Designing Interactive Systems.New York,NY:ACM,2006:271-280.
[87]Tuch A N,Roth S P,Hornbæk K,Opwis K,Bargas-Avila J A.Is beautiful really usable?Toward understanding the relation between usability,aesthetics,and affect in HCI[J].Computers in Human Behavior,2012,28(5):1596-1607.
[88]Zaharias P,Poylymenakou A.Developing a usability evaluation method for e-learning applications:beyond functional usability[J].International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction,2009,25(1):75-98.
[89]Ozkan S,Koseler R.Multi-dimensional students'evaluation of e-learning systems in the higher education context:an empirical investigation[J].Computers&Education,2009,53(4):1285-1296.
[90]Xiao B,Benbasat I.E-commerce product recommendation agents:use,characteristics,and impact[J].MIS Quarterly,2007,31(1):137-209.
[91]Ozok A A,Fan Q,Norcio A F.Design guidelines for effective recommender system interfaces based on a usability criteria conceptual model:results from a college student population[J].Behaviour&Information Technology,2010,29(1):57-83.
[92]Knijnenburg B P,Willemsen M C,Gantner Z,Soncu H,Newell C.Explaining the user experience of recommender systems[J].User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction,2012,22(4-5):441-504.
[93]Ozok A A,Fan Q,Norcio A F.Design guidelines for effective recommender system interfaces based on a usability criteria conceptual model:results from a college student population[J].Behaviour&Information Technology,2010,29(1):57-83.
[94]Park J,Jeong D.An empirical study on Web based question-answer services[J].Journal of the Korean Society for Information Management,2004,21(3):83-98.
[95]Thong J Y L,Hong W,Tam K-Y.Understanding user acceptance of digital libraries:what are the roles of interface characteristics,organizational context,and individual differences[J].Human Computer Study,2002,57(3):215-242.
[96]Fox E A,Hix D,Nowell L T,Brueni D J.Users,user interfaces,and objects:envision a digital library[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science,1993,44:480-491.
[97]Mahlke S,Thuring M.Usability,aesthetics and emotions in humantechnology interaction[J].International Journal of Psychology,2007,42(4):253-264.
[98]Davis F D.Perceived usefulness,perceived ease of use,and user acceptance of information technology[J].MIS Quarterly,1989,13(3):319-340.
[99]Davis F D,Bagozzi R P,Warshaw P R.Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace[J].Journal of Applied Social Psychology,1992,22(14):1111-1132.
[100]Thong J Y L,Hong W,Tam K-Y.Understanding user acceptance of digital libraries:what are the roles of interface characteristics,organizational context,and individual differences[J].Human Computer Study,2002,57(3):215-242.
[101]赵慧文.网络用户体验及互动设计[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2012:142.
[102]Myers J.Cooperative learning in heterogeneous classes[J].Cooperative Learning,1991,11(4):36-48.
[103]Robey D.The paradoxes of transformation[C]//C Sauer,Yetten,Philip and Associates(Eds.).Steps to the Future.San Francisco,CA:Jossey-Bass,1997:209-229.
[104]Hassenzahl M.The thing and I:understanding the relationship between user and product[C]//M A Blythe,K Overbeeke,A F Monk,P C Wright(Eds.).Funology:From Usability to Enjoyment.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Kluwer,2003:31-42.
[105]Mahlke S,Thuring M.Usability,aesthetics and emotions in humantechnology interaction[J].International Journal of Psychology,2007,42(4):253-264.
[106]Yu S-L.Toward a new knowledge sharing community:collective intelligence and learning through Web-based question-answer services[D].Washington,DC:Georgetown University,2006.
[107]Park J,Jeong D.An empirical study on web based question-answer services[J].Journal of the Korean Society for Information Management,2004,21(3):83-98.
[108]Hassenzahl M.The thing and I:understanding the relationship between user and product[C]//M A Blythe,K Overbeeke,A F Monk,P C Wright(Eds.).Funology:From Usability to Enjoyment.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Kluwer,2003:31-42.
[109]Davis F D,Bagozzi R P,Warshaw P R.Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace[J].Journal of Applied Social Psychology,1992,22(14):1111-1132.
[110]Hassenzahl M,Platz A,Burmester M,Lehner K.Hedonic and ergonomic quality aspects determine a software's appeal[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.New York,NY:ACM,2000:201-208.
[111]Mahlke S.Factors influencing the experience of website usage[C]//Proceedings of CHI'02 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems.New York,NY:ACM,2002:846-847.
[112]Schaik P V,Ling J.Modelling user experience with web sites:usability,hedonic value,beauty and goodness[J].Interacting with Computers,2008,20(3):419-432.
[113]Park J,Han S H,Kim H K,Oh S,Moon H.Modeling user experience:a case study on a mobile device[J].International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics,2013,43(2):187-196.
[114]Thong J Y L,Hong W,Tam K-Y.Understanding user acceptance of digitallibraries:what are the roles of interface characteristics,organizational context,and individual differences[J].Human Computer Study,2002,57(3):215-242.
[115]Paechter M,Maier B,Macher D.Students'expectations of,and experiences in elearning:their relation to learning achievements and course satisfaction[J].Computers&Education,2010,54(1):222-229.
[116]Paechter M,Maier B,Macher D.Students'expectations of,and experiences in elearning:their relation to learning achievements and course satisfaction[J].Computers&Education,2010,54(1):222-229.
[117]Shah C,Pomerantz J,Crestani F,Marchand-maillet S,Phane Chen H,Efthimiadis E N.Evaluating and predicting answer quality in community Q&A[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.New York,NY:ACM,2010:411-418.
[118]Kim S,Oh S.Users'relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[119]Davis F D.Perceived usefulness,perceived ease of use,and user acceptance of information technology[J].MIS Quarterly,1989,13(3):19-340.
[120]Schaik P V,Ling J.Modelling user experience with web sites:usability,hedonic value,beauty and goodness[J].Interacting with Computers,2008,20(3):419-432.
[121]Davis F D,Bagozzi R P,Warshaw P R.Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace[J].Journal of Applied Social Psychology,1992,22(14):1111-1132.
[122]Schaik P V,Ling J.Modelling user experience with web sites:usability,hedonic value,beauty and goodness[J].Interacting with Computers,2008,20(3):419-432.
[123]Park J,Han S H,Kim H K,Oh S,Moon H.Modeling user experience:a case study on a mobile device[J].International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics,2013,43(2):187-196.
[124]Anderson J,Gerbing D W.Structural equation modeling in practice:a review and recommended two-step approach[J].Psychological Bulletin,1988,103(3):411-423.
[125]Fornell C,Larcker D F.Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error:algebra and statistics[J].Journal of Marketing Research,1981,18(3):382-388.
[126]Chin W W.The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling[J].Modern methods for Business Research,1998,295(2):295-336.
[127]Hair J F,Black W C,Babin B J,Anderson R E.Multivariate data analysis(7th.ed.)[C].Englewood Cliffs,NJ:Prentice Hall,2010.
[128]Petter S,Straub D,Rai A.Specifying formative constructs in information systems research[J].MIS Quarterly,2007,31(4):623-656.
[129]Podsakoff P M,Organ D W.Self-reports in organizational research:problems and prospects[J].Journal of Management,1986,12(4):531-544.
[130]Thong J Y L,Hong W,Tam K-Y.Understanding user acceptance of digitallibraries:what are the roles of interface characteristics,organizational context,and individual differences[J].Human Computer Study,2002,57(3):215-242.
[131]Davis F D,Bagozzi R P,Warshaw P R.Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace[J].Journal of Applied Social Psychology,1992,22(14):1111-1132.
[132]Mahlke S,Thuring M.Usability,aesthetics and emotions in humantechnology interaction[J].International Journal of Psychology,2007,42(4):253-264.
[133]Myers J.Cooperative learning in heterogeneous classes[J].Cooperative Learning,1991,11(4):36-48.
[134]Knijnenburg B P,Willemsen M C,Gantner Z,Soncu H,Newell C.Explaining the user experience of recommender systems[J].User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction,2012,22(4-5):441-504.
[135]Hassenzahl M.The thing and I:understanding the relationship between user and product[C]//M A Blythe,K Overbeeke,A F Monk,P C Wright(Eds.).Funology:From Usability to Enjoyment.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Kluwer,2003:31-42.
[136]Mahlke S,Thuring M.Usability,aesthetics and emotions in humantechnology interaction[J].International Journal of Psychology,2007,42(4):253-264.
[137]张兴刚,袁毅.基于搜索引擎的中文问答社区比较研究[J].图书馆学研究,2009(6):66-72.
[138]Kim S,Oh S.Users'relevance criteria for evaluating answers in a social Q&A site[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009,60(4):716-727.
[139]Park J,Jeong D.An empirical study on web based question-answer services[J].Journal of the Korean Society for Information Management,2004,21(3):83-98.
[140]iResearch.The research on knowledge question&answer platforms[EB/OL].[2016-10-20].http://tech.china.com/zh_cn/news/net/domestic/11066127/20100618/15985713.html.
[141]Davis F D.Perceived usefulness,perceived ease of use,and user acceptance of information technology[J].MIS Quarterly,1989,13(3):19-340.
[142]Xiao B,Benbasat I.E-commerce product recommendation agents:use,characteristics,and impact[J].MIS Quarterly,2007,31(1):137-209.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。






