网络舆情信息分析与利用过程是一个开放的循环过程,按照信息加工过程各个环节,根据舆情信息的传播与扩散过程,本研究探索构建网络舆情信息分析与利用模型,将信息生命周期融入决策、网络舆情自动化监控过程中,整合内部、外部、人力和社会关系网络等各类资源,形成决策证据链,同时也对分析与利用网络舆情信息的主要方法进行归纳和总结。
3.4.2.1 网络舆情信息生命周期
所谓网络舆情信息的生命周期是指从决策工作产生对网络舆情信息的需求开始,经过舆情信息获取、分析,到舆情信息分析结果被决策者利用的整个过程,如图3-9所示。
在网络舆情信息分析与利用实际工作中,确定某一时期内的舆情信息管理主题是舆情信息分析与利用的基础,一般来说确定主题的过程是一个情报循环的过程,首先根据舆情信息需求提出选题,确定分析舆情信息主题的可行性,再确定信息主题的选择,然后制定具体的舆情信息分析与利用工作方案,以上步骤环环相扣。

图3-9 网络舆情信息生命周期
3.4.2.2 网络舆情信息分析与利用模型
本研究将Herring模型[110]引入到网络舆情信息工作中,结合网络舆情信息生命周期及决策过程,提出一个由工作框架、系统层和流程层构成的支持网络舆情信息分析与利用系统建立和运作的概念模型。
(1)网络舆情信息分析与利用工作框架模型
在现代社会管理环境中,决策者和舆情信息分析人员必须要知道:第一,在多大程度上能够理解为什么和如何与影响民众情绪的因素进行互动?第二,如果舆情在决策层流动,决策者是否真正使用了这些信息?这一整体过程其实是从信息分析过程进入了辅助决策过程。决策者与舆情信息分析人员分别作为舆情信息分析与利用工作最重要的两种角色,如何实现需求与成果之间的无缝连接,是网络舆情信息分析与利用实践中最关键的一个环节。本研究提出的网络舆情信息分析与利用工作框架层由五层组成,模型以决策、信息需求、舆情信息分析、舆情信息利用、信息来源等因素建立起两组参与者的联系(如图3-10所示)。决策制定者根据战略制定、战术制定和操作制定等特点,确定对网络舆情信息的需求,包括涉及的事件、人物、时间、地点,事件发生的原因、事件发展状态等,再开展一系列舆情活动,包括准确评估舆情信息监测价值及优先级、及时确认回应机会、正确认识舆情带来的管理危机、有效引导与控制舆情事件发展等,在制定决策的过程中需要相关辅助信息如意见领袖、公众意见分类和趋势预测报告等,舆情信息分析人员据此寻找信息来源,运用一次信息和二次信息、显性知识和隐性知识等进行网络舆情信息的采集、整合与分析,以满足决策者对网络舆情信息的需求。
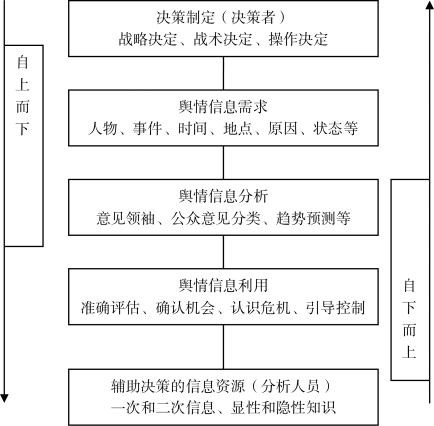
图3-10 网络舆情信息分析与利用工作框架模型
(2)网络舆情信息分析与利用模型的系统层及技术结构
系统层是开展网络舆情信息活动的保障,提供了用舆情信息资源满足用户需求的工作模式。网络舆情信息分析与利用系统要实现从网络信息资源中挖掘出有价值的网络舆情,并提供给决策者使用,以辅助决策,则需要有效集成网络舆情信息采集技术、网络舆情信息预处理技术、网络舆情信息分析技术和网络舆情信息服务技术,这些技术相互支撑,共同形成网络舆情信息分析与利用模型的系统层(如图3-11所示),以支持系统的高效运行。

图3-11 网络舆情信息分析与利用模型的系统层及技术结构
(3)网络舆情信息分析与利用模型的流程层模型
网络舆情信息分析与利用过程是关于网络突发异常事件给管理带来的威胁、寻找回应机会的舆情信息加工过程,主要包括组织协调、信息采集、信息预处理、信息分析、生成报告和发布报告六个环节,这六个环节根据网络舆情事件的演进和明确,反复迭代、重复。
由图3-12所示,流程层模型反映了网络舆情信息分析与利用系统的具体操作过程,可以划分为三个阶段:
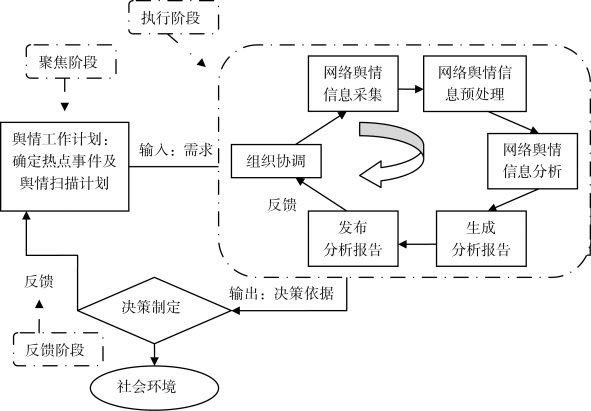
图3-12 网络舆情信息分析与利用模型的流程层模型
流程层揭示了工作框架中资源层级、舆情信息需求层级和舆情活动层级之间的关系,是对现实世界中舆情信息分析与利用工作流的抽象与概括,也是网络舆情信息分析与利用自动化系统设计中数据流的概念模型。
【注释】
[1]Taylor S R.Question-negotiation an information-seeking in libraries[J].College and Research Libraries,1968,29(3):178-194.
[2]Belkin N J.Anomalous state of knowledge for information retrieval[J].Canadian Journal of Information Science,1980:5.
[3]艾新革.政府舆情信息需求理论初探[J].图书馆论坛,2011,31(2):9-13.
[4]Dervin B L,Foremanwernet L,Lauterbach E.Sense-making methodology reader:Selected writings of brenda dervin[J].2003.
[5]严怡民,等.现代情报学理论[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社,1996:89-90.
[6]马费成.论情报学的基本原理及理论体系构建[J].情报学报,2007,26(1):3-13.
[7]Culnan M J.Chauffeured versus end user access to commercial databases:The effects of task and individual differences[J].Mis Quarterly,1983,7(1):55-67.
[8]Daft R L,Lengel R H.Organizational information requirements,media richness and structuraldesign[J].Management Science,1986,32(5):554-571.
[9]Wilson T.Exploring models of information behaviour:The“uncertainty”project[J].Information Processing&Management,1999,35(6):839-849.
[10]Allen D.Information behavior and decision making in time-constrained practice:A dual-processing perspective[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science&Technology,2011,62(11):2165-2181.
[11]信息分析[EB/OL].[2016-01-21].http://wiki.mbalib.com/wiki/信息分析.
[12]信息加工[EB/OL].[2016-01-21].http://wiki.mbalib.com/wiki/信息加工.
[13]凯斯.寻找信息[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2018:111.
[14]梁战平.情报学若干问题辨析[J].情报理论与实践,2003,26(3):193-198.
[15]孟广均,徐引篪.国外图书馆学情报学研究进展[M].北京:北京图书馆出版社,1999:161-167.
[16]马费成.IRM-KM范式与情报学发展研究[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社,2008:134.
[17]Taylor S R.Question-negotiation an information-seeking in libraries[J].College and Research Libraries,1968,29(3):178-194.
[18]马费成.IRM-KM范式与情报学发展研究[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社,2008:134.
[19]Zeleny M.Management support systems:Towards integrated knowledge management[J].Human Systems Management,1987,7(1):59-70.
[20]FrickéM.The knowledge pyramid:A critique of the DIKW hierarchy[J].Journal of Information Science,2009,35(6):131-142.
[21]Mittelstrass J.The loss of knowledge in the information age[J].From Information to Knowledge,from Knowledge to wisdom:Challenges and changes facing higher education in the digital age/de Corte,Erik et al.(Hrsg.).London:Portland Press,2010:-S.19-23.
[22]数据[EB/OL].[2016-01-18].http://www.baike.baidu.com.
[23]Ackoff R L.From data to wisdom[J].Journal of Applied Systems Analysis,1989:170-172.
[24]马费成,等.信息管理学基础[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社,2002:7.
[25]马费成.IRM-KM范式与情报学发展研究[M].武汉:武汉大学出版社,2008:134.
[26]Rowley J.The wisdom hierarchy:Representations of the DIKW hierarchy[J].Journal of Information Science,2007,33(2):163-180.
[27]Targowski A.From Data to Wisdom[J].Dialogue&Universalism,2005,15(5):55-71.
[28]Ackoff R L.From Data to Wisdom[J].Journal of Applied Systems Analysis,1989:170-172.
[29]Mittelstrass J.The loss of knowledge in the information age[J].From Information to Knowledge,from Knowledge to Wisdom:Challenges and Changes Facing Higher Education in the Digital age/de Corte,Erik et al.(Hrsg.).London:Portland Press,2010:-S.19-23.
[30]钟义信.信息科学原理(第3版)[M].北京:北京邮电大学出版社,2002:189.
[31]Ackoff R L.From data to wisdom[J].Journal of Applied Systems Analysis,1989:170-172.
[32]Rowley J.Where is the wisdom that we have lost in knowledge?[J].Journal of Documentation,2006,62(2):251-270.
[33]Zeleny M.Knowledge-information autopoietic cycle:Towards the wisdom systems[J].International Journal of Management&Decision Making,2006(7):3-18.
[34]Targowski A.From data to wisdom[J].Dialogue&Universalism,2005,15(5):55-71.
[35]Kasperson R E.Integrating Science and Policy[J].Integrating Science and Policy:Earthscan,2011:1063-1068.
[36]Jennex M E.Re-Visiting the knowledge pyramid[J].2009:1-7.
[37]Spiekermann R,Kienberger S,Norton J,et al.The disaster-knowledge matrixreframing and evaluating the knowledge challenges in disaster risk reduction[J].International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction,2015,13:96-108.
[38]Spiekermann R,Kienberger S,Norton J,et al.The disaster-knowledge matrixreframing and evaluating the knowledge challenges in disaster risk reduction[J].International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction,2015,13:96-108.
[39]Davenport T H,Prusak L,Prusak L.Working knowledge:How organizations manage what they know[J].Ubiquity,2001,26(4):396-397.
[40]皮尔斯·李斯卡,赵星植.皮尔斯:论符号[M].成都:四川大学出版社,2014.
[41]Alon Friedman,Martin Thellefsen.Concept theory and semiotics in knowledge organization[J].Journal of Documentation,2011,67(4):644-674.
[42]Zeng Lei,Athena S.Toward an international sharing and use of subject authority data[EB/OL].[2014-05-18].http://www.oclc.org/research/events/frbrworkshop/presen tations/zeng/Zeng_Salaba.ppt.
[43]陈烨,赵一鸣,姜又琦.基于关联数据的知识组织研究述评[J].情报理论与实践,2016,39(2):139-144.
[44]王向前,张宝隆,李慧宗.本体研究综述[J].情报杂志,2016,35(6):163-170.(https://www.daowen.com)
[45]邓志鸿,唐世渭,张铭,杨冬青,陈捷.Ontology研究综述[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2002(5):730-738.
[46]Gruber T R.Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing?[J].International Journal of Human Computer Studies,1995,43(5-6):907-928.
[47]Studer R,Benjamins V R,Fensel D.Knowledge engineering,principles and methods[J].Data and Knowledge Engineering,1998,25(1-2):161-197.
[48]汤艳莉,赖茂生.Ontology在自然语言检索中的应用研究[J].现代图书情报技术,2005(2):33-36,52.
[49]张晓林,李宇.描述知识组织体系的元数据[J].图书情报工作,2002(2):64-69.
[50]Perez A G,Benjamins V R.Overview of Knowledge Sharing and Reuse Components:Ontologies and Problem-Solving Methods[C].Stockholm V R,Benjamins B,Chandrasekaran A,eds.Proceedings of the IJCAI-99 workshop on Ontologies and Problem-SolvingMethods(KRR5),1999:1-15.
[51]徐荣生.知识单元初论[J].图书馆杂志,2001(7):2-5.
[52]赵蓉英,张心源.基于知识元抽取的中文智库成果描述规则研究[J].图书与情报,2017(1):119-127.
[53]温有奎,焦玉英.基于知识元的知识发现[M].西安:西安电子科技大学出版社,2011.
[54]赵蓉英,张心源.基于知识元抽取的中文智库成果描述规则研究[J].图书与情报,2017(1):119-127.
[55]赵红州,蒋国华.知识单元与指数规律[J].科学学与科学技术管理,1984(9):39-41.
[56]文庭孝,侯经川,龚蛟腾,刘晓英,汪全莉.中文文本知识元的构建及其现实意义[J].中国图书馆学报,2007(6):91-95.
[57]Olejniczak K,Raimondo E,Kupiec T.Evaluation units as knowledge brokers:Testing and calibrating an innovative framework[J].Evaluation,2016,22(2):168-189.
[58]陆汝钤,金芝.从基于知识的软件工程到基于知件的软件工程[J].中国科学:E辑,2008,38(6):843-863.
[59]高继平,丁堃,潘云涛,等.知识元研究述评[J].情报理论与实践,2015,38(7):134-138.
[60]傅柱,王曰芬,徐绪堪,关鹏,丁绪辉.基于知识元的中文专利文献知识描述框架[J].情报理论与实践,2019,42(4):145-150.
[61]王崇德,李美.论超文本信息系统[J].中国图书馆学报,1996(4):30-35.
[62]温有奎,温浩,徐端颐,等.基于知识元的文本知识标引[J].情报学报,2006(3):282-288.
[63]王昊奋,漆桂林,陈华钧.知识图谱:方法、实践与应用[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2019.
[64]王兰成,娄国哲.基于知识图谱的网络舆情管理方法与实践研究[J/OL].[2020-02-10].情报理论与实践:1-7.http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1762.G3.20191223.0858.002.html.
[65]赵一鸣.知识图谱是一种知识组织系统吗?[J].图书情报知识,2017(5):2.
[66]漆桂林,高桓,吴天星.知识图谱研究进展[J].情报工程,2017,3(1):4-25.
[67]Zhou Z Q,Qi G L,Glimm B.Exploring parallel tractability of ontology materialization[C].European Conference on Artificial Intelligence,Hague,Netherlands,August 29-September 2,2016:73-81.
[68]谢科范,赵湜,陈刚,等.网络舆情突发事件的生命周期原理及集群决策研究[J].武汉理工大学学报(社会科学版),2010,23(4):482-486.
[69]易臣何.突发事件网络舆情的演化规律与政府监控[D].湘潭大学,2014:71-82.
[70]高青苗.网络舆情的生成演变与应对的现实困境研究[D].重庆大学,2013:99-108.
[71]罗伯特·希斯.危机管理[M].北京:中信出版社,2004:207.
[72]Litvaj I,Stancekova D.Decision-making,and their relation to the knowledge management,use of knowledge management in decision-making[J].Procedia Economics&Finance,2015,23:467-472.
[73]刘心报.决策分析与决策支持系统[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2009.
[74]西蒙.管理行为(珍藏版)[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2013:107-120.
[75]郎淳刚,刘树林.国外自然决策理论研究述评[J].技术经济与管理研究,2009,4:63-66.
[76]Klein G.A Recognition-Primed Decision(RPD)Model of Rapid Decision Making[M].US:New Jersey,Ablex Publishing,1993.
[77]Hutton R J B,Klein G.Expert decision making[J].Systems Engineering,1999,2(2):32-45.
[78]Randel J M,Pugh H L,Reed S K.Differences in expert and novice situation awareness in naturalistic decision making[J].International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,1996,45(5):579-597.
[79]Means B,Salas E,Crandall B,Jacobs T O.Training Decision-Makers for the Real World[M]//Klein G,Orasanu J,Calderwood R,Zsambok C,eds.Decision Making in Action:Models and Methods Norwood,NJ:Ablex,1993:306-326.
[80]Klein G.Sources of Power:How People Make Decisions[M].Cambridge,MA:MIT Press,1998:104-113.
[81]Glaser R.Thoughts on Expertise[M]//Schooler C,Schaie W,eds.Cognitive Functioning and Social Functioning over the Life Course,Norwood,NJ:Ablex,1987:81-94.
[82]Kirkwood A.Discounting the unexpected:The limitations of isomorphic thinking[J].Risk Management,1999,1(4):33-44.
[83]Klein G.Sources of Power:How People Make Decisions[M].Cambridge,MA:MIT Press,1998:104-113.
[84]Saracevic A,Zhang Z,Kusunoki D.Decision making tasks in time-critical medical settings[C].GROUP 12,ACM,Florida,2012.
[85]Weick B K E.The collapse of sensemaking in organizations-The Man Gulch Disaster[C].2013:628-652.
[86]Court A W.The relationship between information and personal knowledge in new product development[J].International Journal of Information Management,1997,17(2):123-138.
[87]王绍光.中国公共政策议程设置的模式[J].中国社会科学,2006(5):42-56.
[88]吴娟.地方政府应对网络舆情的联动应急机制研究[D].华中师范大学,2013:47-49.
[89]辛立艳.面向政府危机决策的信息管理机制研究[D].吉林大学,2014:130-142.
[90]信息分析[EB/OL].[2011-07-21].http://baike.baidu.com/view/1355865.htm.
[91]信息加工过程[EB/OL].[2011-07-21].http://baike.baidu.com/view/21659 50.htm.
[92]活动理论[EB/OL].[2016-01-21].www.baike.baidu.com.
[93]王知津,韩正彪,周鹏.活动理论视角下的情报学研究及转向模型[J].图书情报知识,2012(1):4-14.
[94]Gordon Wells.The role of dialogue in activity theory[J].Mind Culture&Activity,2002,9(1):43-66.
[95]Allen D,Karanasios S,Slavova M.Working with activity theory:Context,technology,and information behavior[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science&Technology,2011,62(4):776-788.
[96]Chen R,Sharman R,Chakravarti N,et al.Emergency Response Information System Interoperability:Development of Chemical Incident Response Data Model[J].Journal of the Association for Information Systems,2008,9:200-230.
[97]Kutti K.Activity Theory,Transformation of Work,and Information Systems Design[M]//Engeström Y,Miettinen R,Punamaki R L,eds.Perspectives on Activity Theory.Cambridge University Press,New York,1999:360-376.
[98]Lim C P,Hang D.An activity theory approach to research of ICT integration in Singaporeschools[J].Computers&Education,2003,41(1):49-63.
[99]Wilson T D.A re-examination of information seeking behaviour in the context of activity theory[J].Information Research,2015,11(4).
[100]Allen D,Karanasios S,Slavova M.Working with activity theory:Context,technology,and information behavior[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science&Technology,2011,62(4):776-788.
[101]Yi-Chen.Web-Using behavior in context of the home use environment:Toward a multidimensional framework[J].Journal of Library&Information Science,2008,34(2).
[102]Engeström Y.Activity theory as a framework for analyzing and redesigning work[J].Ergonomics,2010,43(7):960-974.
[103]Behrend M.Engeström's activity theory as a tool to analyse online resources embedding academic literacies[J].Journal of Academic Language&Learning,2014.
[104]Ibrahim N H,Allen D.Information sharing and trust during major incidents:Findings from the oil industry[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science&Technology,2012,63(63):1916-1928.
[105]Othman S H,Beydoun G.Model-driven disaster management[J].Information&Management,2013,50(5):218-228.
[106]Korpela M,Mursu A,Soriyan H A.Information systems development as an activity[J].Computer Supported Cooperative Work,2002,11(1-2):111-128.
[107]Werner Kuhn.Ontologies in support of activities in geographical space[J].International Journal of Geographical Information Science,2001,Volume 15(7):613-631(19).
[108]O'Leary D E.An activity theory analysis of RFID in hospitals[J].International Journal of Applied Logistics,2010,1(2):64-81.
[109]王知津,韩正彪,周鹏.活动理论视角下的情报学研究及转向模型[J].图书情报知识,2012(1):4-14.
[110]Herring J P.Key intelligence topics:a process to identify and define intelligence needs[J].Competitive Intelligence Revies,1999,10(2):4-14.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。







