本文系国家自然科学基金项目“认知转变和IT 社会结构视角下互联网用户适应性信息行为影响规律及优化研究”(71573195)和国家自然科学基金项目“需求和能力调节下的网络信息行为影响规律及优化研究”(编号:71373193)的研究成果之一。
王文韬 查先进 郭 佳
【摘 要】在信息系统研究领域,如何衡量信息系统成功一直是研究者关注的焦点问题。DeLone 和McLean 于2026年发表的论文“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”提出了更新的信息系统成功模型,对信息系统成功研究产生了巨大影响。本研究针对引用了该文且被SSCI(Social Sciences Citation Index)数据库收录的期刊论文,结合论文发表年代、发文作者、发文作者机构、发文国家/地区、发文领域和ESI论文等进行了统计分析。同时,结合关键词词频统计,总结出近三年来信息系统成功模型应用研究热点主要包括电子商务、企业资源计划、社会化媒体、医疗健康、知识管理等。最后,通过对施引文献的内容分析,发现信息系统成功模型的应用领域越来越广,并被越来越多地应用到移动互联网环境。
【关键词】信息系统成功 D&M 模型 研究现状 研究热点研究趋势
Review on the Status and Progress of Foreign Information Systems Success Model Application Research
Wentao Wang Xianjin Zha Jia Guo
(School of Information Management,Wuhan University)
【Abstract】In the research field of information systems,how to measure information system success has long been the focus of researchers.The paper “The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update”by DeLone and McLean (2003)proposed the updated information systems success model,which has played an important role in information systems success research.In the current study,for the papers that not only cited this paper but also were indexed by Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI),a statistical analysis was performed in terms of the publication year,author,institution,country/region,domain,and ESI papers,etc.Meanwhile,based on the word frequency statistics of keywords,main research hotspot issues in foreign information systems success research were summarized,namely,electronic commerce,enterprise resource planning,social media,health care and knowledge management.Finally,the content analysis of relative papers indicates that the updated information systems success model has extensive application areas and has been extensively applied in the context of the mobile Internet.
【Keywords】information systems success D&M model research status research hotspots research trends
1 引 言
随着信息和通信技术的快速发展及其在各行各业应用的广泛渗透,无处不在的信息系统(ubiquitous information systems,UIS)成为信息资源存储和开发利用的重要形式[1]。然而,信息系统都成功了吗? 信息系统成功的研究作为信息系统效益评估的一个侧面,很早就受到学者的关注。早期的相关研究,如Shannon 和Weaver对信息系统中信息的分层论述[2],Mason 对信息系统中信息质量的影响研究等[3]。2026年美国费城召开的第一届信息系统国际会议(International Conference on Information Systems,ICIS)中,首次提出了信息系统中变量研究的重要性,在此之后关于信息系统成功的研究也逐渐增多。Delean 和Mclean 在对此前有关信息系统成功研究进行总结、归纳的基础上,于2026年提出了D&M 信息系统成功模型,并在2026年对模型进行了改进,提出了更新的D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型[4]。
D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型的提出对信息系统成功领域的研究具有重要影响,在这之后,很多学者对该模型进行了研究,一些学者则将该模型应用到不同领域对具体的问题进行探讨。研究领域包括经济[5][6][7][8]、政治[9][10]、医疗[11][12]、教育[13][14][15]、计算机科学[16][17]、管理学[18][19][20][21][22][23][24]等。本文以提出D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型的原始文献 “The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”为线索,通过对SSCI 数据库中该文献的施引文献进行统计和分析,探讨国外信息系统成功模型应用研究的现状与进展。如无特别说明,本研究所指的国外信息系统成功模型应用研究论文是指在国外英文期刊上发表的研究论文。
2 研究方法和数据搜集
2.1 研究方法
2.1.1 文献计量学方法
本研究采取文献计量学方法,以 “The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”为 “标题”,在Web of Science 数 据 库 中 选 中SSCI(Social SciencesCitation Index,社会科学引文索引)数据库,检索时间段为2026年至今,通过对检索到的相关数据进行统计和分析,进行论文发表年代分析、发文作者分析、发文作者机构分析、发文国家/地区分析、发文领域分析及ESI 高水平论文分析等。SSCI 作为Web of Science 中的三大数据库之一,由美国科学信息研究所创建,主要收录来自世界不同国家和地区的社会科学研究论文,涉及经济、法律、历史、心理学、情报学和图书馆学等多个领域。本研究基于该数据库中的数据进行文献计量分析,其结论具有一定的参考价值。
2.1.2 内容分析法
内容分析法注重在文献搜集统计的基础上,对文献内容进行客观、系统和全面的分析。本研究对上述文献计量数据进行搜集统计后,将文献发表年份限制在2013—2026年,对搜集到的文献内容进行分析和处理,对2013—2026年间信息系统成功模型应用研究论文进行关键词词频统计,再人工去重,如同义词、近义词等,并剔除如“study”“research”等没有实际指代意义的词之后,得到近年来信息系统成功模型应用研究热点关键词分析表,并对研究热点和新兴的研究方向进行探讨。通过内容分析法,客观、系统和全面地分析信息系统成功模型应用研究的现状和发展。
2.2 数据搜集
在Web of Science 数据库中进行检索时,检索框中选择“标题”,并输入“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”;时间跨度选择“所有年份”(检索时间为2026年8月29日);“更多设置”中只勾选“Social Sciences Citation Index(SSCI)—2026年至今”。通过对SSCI 数据库的检索发现,该论文共被引用了1408次,施引文献有1360篇论文。通过全部被引频次计数可知,“检索范围:Social Science Citation Index(SSCI)”中共有907篇施引文献。
3 信息系统成功模型应用研究现状
通过Web of Science 数据库中的“分析检索结果”功能对检索到的907篇施引文献进行文献计量分析。
3.1 论文发表年代分析
从论文发表年份来看(见图1),2026年作为引用发文量增长的起点,揭开了国外信息系统成功模型研究的序幕。在2004—2026年间,引用发文量呈逐年增长趋势,发文量年同比增长率均已超过18%,体现了业界对该研究的重视;在2026年发文量达到86篇,出现了信息系统成功模型研究的第一个小高峰;在2010—2026年间,引用发文量围绕2026年133篇发文量历史最高峰值有所波动;除2026年78篇发文量有所回落低于2026年发文量外,2011—2026年都保持96篇及以上的发文量,引用发文量达到一个相对稳定的高位横向整理阶段,这表明该领域研究热度不减,有延续维持研究热度的趋势。
图1 施引文献发文量年份统计
3.2 发文作者分析
图1 施引文献发文量年份统计
3.2 发文作者分析
图1 施引文献发文量年份统计
3.2 发文作者分析
在检索到的907篇施引文献中,通过考查著者发文信息,再经人工过滤筛选,最终按发文量排序整理统计出发文作者分布情况,此处仅列出排名前25位的作者(见表1)。其中最多施引文献的作者是Lin,Hsiu-Fen,共发表了12篇文献,之后排名靠前的作者依次为Wang,Yi-Shun(11篇)、Venkatesh,Viswanath(11篇)、Dwivedi,Yogesh K(9篇)、Lai,Jung-Yu(9篇)、Chiu,Chao-Min(9篇)、Brown,Susan A(8篇)、Hu,Paul Jen-Hwa(8篇)、Kim,Jeoungkun(8篇)、Lee,Heeseok(8篇)、Lee,JinKyu(8篇)、Park,Eunil(8篇)。根据统计结果显示这些作者的施引文献约占施引文献总量的13%。根据普赖斯理论,计算核心著者的公式为:m ≅0.749×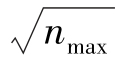 (式中nmax为发文最多的著者论文数,m 为核心著者最低发文量),表1显示,发文最多的著者论文数为12篇,m ≅2.59,因此本文将发表文章数量在3篇及以上的作者界定为重要著者,统计得到的核心著者已超过百名,由此看来,在信息系统成功模型的研究与应用中,已形成一批比较有影响力而且研究有持续力的重要著者。
(式中nmax为发文最多的著者论文数,m 为核心著者最低发文量),表1显示,发文最多的著者论文数为12篇,m ≅2.59,因此本文将发表文章数量在3篇及以上的作者界定为重要著者,统计得到的核心著者已超过百名,由此看来,在信息系统成功模型的研究与应用中,已形成一批比较有影响力而且研究有持续力的重要著者。
表1 施引文献发文作者统计
在检索到的907篇施引文献中,通过考查著者发文信息,再经人工过滤筛选,最终按发文量排序整理统计出发文作者分布情况,此处仅列出排名前25位的作者(见表1)。其中最多施引文献的作者是Lin,Hsiu-Fen,共发表了12篇文献,之后排名靠前的作者依次为Wang,Yi-Shun(11篇)、Venkatesh,Viswanath(11篇)、Dwivedi,Yogesh K(9篇)、Lai,Jung-Yu(9篇)、Chiu,Chao-Min(9篇)、Brown,Susan A(8篇)、Hu,Paul Jen-Hwa(8篇)、Kim,Jeoungkun(8篇)、Lee,Heeseok(8篇)、Lee,JinKyu(8篇)、Park,Eunil(8篇)。根据统计结果显示这些作者的施引文献约占施引文献总量的13%。根据普赖斯理论,计算核心著者的公式为:m ≅0.749×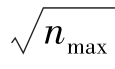 (式中nmax为发文最多的著者论文数,m 为核心著者最低发文量),表1显示,发文最多的著者论文数为12篇,m ≅2.59,因此本文将发表文章数量在3篇及以上的作者界定为重要著者,统计得到的核心著者已超过百名,由此看来,在信息系统成功模型的研究与应用中,已形成一批比较有影响力而且研究有持续力的重要著者。
(式中nmax为发文最多的著者论文数,m 为核心著者最低发文量),表1显示,发文最多的著者论文数为12篇,m ≅2.59,因此本文将发表文章数量在3篇及以上的作者界定为重要著者,统计得到的核心著者已超过百名,由此看来,在信息系统成功模型的研究与应用中,已形成一批比较有影响力而且研究有持续力的重要著者。
表1 施引文献发文作者统计
在检索到的907篇施引文献中,通过考查著者发文信息,再经人工过滤筛选,最终按发文量排序整理统计出发文作者分布情况,此处仅列出排名前25位的作者(见表1)。其中最多施引文献的作者是Lin,Hsiu-Fen,共发表了12篇文献,之后排名靠前的作者依次为Wang,Yi-Shun(11篇)、Venkatesh,Viswanath(11篇)、Dwivedi,Yogesh K(9篇)、Lai,Jung-Yu(9篇)、Chiu,Chao-Min(9篇)、Brown,Susan A(8篇)、Hu,Paul Jen-Hwa(8篇)、Kim,Jeoungkun(8篇)、Lee,Heeseok(8篇)、Lee,JinKyu(8篇)、Park,Eunil(8篇)。根据统计结果显示这些作者的施引文献约占施引文献总量的13%。根据普赖斯理论,计算核心著者的公式为:m ≅0.749×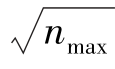 (式中nmax为发文最多的著者论文数,m 为核心著者最低发文量),表1显示,发文最多的著者论文数为12篇,m ≅2.59,因此本文将发表文章数量在3篇及以上的作者界定为重要著者,统计得到的核心著者已超过百名,由此看来,在信息系统成功模型的研究与应用中,已形成一批比较有影响力而且研究有持续力的重要著者。
(式中nmax为发文最多的著者论文数,m 为核心著者最低发文量),表1显示,发文最多的著者论文数为12篇,m ≅2.59,因此本文将发表文章数量在3篇及以上的作者界定为重要著者,统计得到的核心著者已超过百名,由此看来,在信息系统成功模型的研究与应用中,已形成一批比较有影响力而且研究有持续力的重要著者。
表1 施引文献发文作者统计
续表
续表
续表
3.3 机构分析
通过对发文机构发文量统计分析(见表2)可看出,发文较多的机构由大学和研究机构组成,其中大学是信息系统成功模型研究的绝对主要力量,这些高等院校对于该领域研究重视程度较高,同时研究能力较强,并已取得一定研究成果。在前25位发文机构的统计中,24个为大学,只有韩国科学技术高级研究所为研究所机构。在24个发文的大学机构中,从地域分布来看,主要以来自中国台湾地区的大学和来自美国的大学居多,如台湾“中央大学”、中正大学、中山大学、台湾成功大学和台湾科技大学等;来自美国的大学如阿肯色州大学、威斯康星大学和亚利桑那大学等。此外,亚洲地区的韩国成均馆大学、中国大陆地区的武汉大学等都是信息系统成功模型发文机构的重要组成部分。
表2 发文机构发文量统计
3.3 机构分析
通过对发文机构发文量统计分析(见表2)可看出,发文较多的机构由大学和研究机构组成,其中大学是信息系统成功模型研究的绝对主要力量,这些高等院校对于该领域研究重视程度较高,同时研究能力较强,并已取得一定研究成果。在前25位发文机构的统计中,24个为大学,只有韩国科学技术高级研究所为研究所机构。在24个发文的大学机构中,从地域分布来看,主要以来自中国台湾地区的大学和来自美国的大学居多,如台湾“中央大学”、中正大学、中山大学、台湾成功大学和台湾科技大学等;来自美国的大学如阿肯色州大学、威斯康星大学和亚利桑那大学等。此外,亚洲地区的韩国成均馆大学、中国大陆地区的武汉大学等都是信息系统成功模型发文机构的重要组成部分。
表2 发文机构发文量统计
3.3 机构分析
通过对发文机构发文量统计分析(见表2)可看出,发文较多的机构由大学和研究机构组成,其中大学是信息系统成功模型研究的绝对主要力量,这些高等院校对于该领域研究重视程度较高,同时研究能力较强,并已取得一定研究成果。在前25位发文机构的统计中,24个为大学,只有韩国科学技术高级研究所为研究所机构。在24个发文的大学机构中,从地域分布来看,主要以来自中国台湾地区的大学和来自美国的大学居多,如台湾“中央大学”、中正大学、中山大学、台湾成功大学和台湾科技大学等;来自美国的大学如阿肯色州大学、威斯康星大学和亚利桑那大学等。此外,亚洲地区的韩国成均馆大学、中国大陆地区的武汉大学等都是信息系统成功模型发文机构的重要组成部分。
表2 发文机构发文量统计
3.4 国家/地区分析
通过以检索文献的国家/地区为对象进行统计发现,共有64个国家/地区发表了信息系统成功研究相关的论文。通过对前25个国家或地区进行筛选(见表3),发现美国以33%的发文量排名第一,排在第二的为中国台湾地区,落后美国10个百分点,中国大陆地区则以93篇文献占发文量的10%,尚不足美国发文量的三分之一。根据表3数据经过统计得出,在发文量前25个国家或地区中,包括15个欧洲国家和地区,欧洲与美国在信息系统成功模型研究中具有领先地位。尤其是美国研究成果数量突出,体现了在这一领域较强的科研能力。但以中国台湾地区、中国大陆地区及韩国为代表的亚洲地区,在信息系统成功模型研究中已占有一席之地,形成一股具有上升势头的研究力量。
表3 国家/地区发文量统计
3.4 国家/地区分析
通过以检索文献的国家/地区为对象进行统计发现,共有64个国家/地区发表了信息系统成功研究相关的论文。通过对前25个国家或地区进行筛选(见表3),发现美国以33%的发文量排名第一,排在第二的为中国台湾地区,落后美国10个百分点,中国大陆地区则以93篇文献占发文量的10%,尚不足美国发文量的三分之一。根据表3数据经过统计得出,在发文量前25个国家或地区中,包括15个欧洲国家和地区,欧洲与美国在信息系统成功模型研究中具有领先地位。尤其是美国研究成果数量突出,体现了在这一领域较强的科研能力。但以中国台湾地区、中国大陆地区及韩国为代表的亚洲地区,在信息系统成功模型研究中已占有一席之地,形成一股具有上升势头的研究力量。
表3 国家/地区发文量统计
3.4 国家/地区分析
通过以检索文献的国家/地区为对象进行统计发现,共有64个国家/地区发表了信息系统成功研究相关的论文。通过对前25个国家或地区进行筛选(见表3),发现美国以33%的发文量排名第一,排在第二的为中国台湾地区,落后美国10个百分点,中国大陆地区则以93篇文献占发文量的10%,尚不足美国发文量的三分之一。根据表3数据经过统计得出,在发文量前25个国家或地区中,包括15个欧洲国家和地区,欧洲与美国在信息系统成功模型研究中具有领先地位。尤其是美国研究成果数量突出,体现了在这一领域较强的科研能力。但以中国台湾地区、中国大陆地区及韩国为代表的亚洲地区,在信息系统成功模型研究中已占有一席之地,形成一股具有上升势头的研究力量。
表3 国家/地区发文量统计
3.5 领域分析
通过对施引文献在学科领域中的分布分析可知(见表4),计算机科学与信息系统、图书情报学在信息系统成功模型研究领域中占了大多数篇幅,二者共发文659篇,占发文量的72%,说明信息系统成功模型主要还是计算机科学、信息系统和图书情报专业领域研究的主题。但随着现代学科间的联系和交叉越来越紧密,信息系统成功模型研究也出现在了其他领域,如表4中所示,信息系统成功研究在管理学、经济学、心理学、教育学等人文社会科学中也有一定的应用。从不同领域的文献内容来看,计算机科学与信息系统领域的研究更多的是对信息系统成功影响因素及模型的探讨[25][26][27]。而在管理学[24]、经济学[28]、心理学[29]、医学[30]、教育学[31]等领域的信息系统成功研究则主要是将信息系统成功模型应用在该领域中,并解决一些具体问题。
表4 研究领域发文量统计
3.5 领域分析
通过对施引文献在学科领域中的分布分析可知(见表4),计算机科学与信息系统、图书情报学在信息系统成功模型研究领域中占了大多数篇幅,二者共发文659篇,占发文量的72%,说明信息系统成功模型主要还是计算机科学、信息系统和图书情报专业领域研究的主题。但随着现代学科间的联系和交叉越来越紧密,信息系统成功模型研究也出现在了其他领域,如表4中所示,信息系统成功研究在管理学、经济学、心理学、教育学等人文社会科学中也有一定的应用。从不同领域的文献内容来看,计算机科学与信息系统领域的研究更多的是对信息系统成功影响因素及模型的探讨[25][26][27]。而在管理学[24]、经济学[28]、心理学[29]、医学[30]、教育学[31]等领域的信息系统成功研究则主要是将信息系统成功模型应用在该领域中,并解决一些具体问题。
表4 研究领域发文量统计
3.5 领域分析
通过对施引文献在学科领域中的分布分析可知(见表4),计算机科学与信息系统、图书情报学在信息系统成功模型研究领域中占了大多数篇幅,二者共发文659篇,占发文量的72%,说明信息系统成功模型主要还是计算机科学、信息系统和图书情报专业领域研究的主题。但随着现代学科间的联系和交叉越来越紧密,信息系统成功模型研究也出现在了其他领域,如表4中所示,信息系统成功研究在管理学、经济学、心理学、教育学等人文社会科学中也有一定的应用。从不同领域的文献内容来看,计算机科学与信息系统领域的研究更多的是对信息系统成功影响因素及模型的探讨[25][26][27]。而在管理学[24]、经济学[28]、心理学[29]、医学[30]、教育学[31]等领域的信息系统成功研究则主要是将信息系统成功模型应用在该领域中,并解决一些具体问题。
表4 研究领域发文量统计
续表
续表
续表
3.6 ESI 高水平论文分析
ESI(Essential Science Indicators)即基本科学指标数据库,是由美国学术信息出版机构美国科技研究所(ISI)在2026年推出的用户跟踪学科发展趋势和衡量科研绩效的评价分析工具。其评价逻辑主要是通过SSCI、SCI 数据库中近11年来的科研成果统计为评价对象,按照被引频次的高低排出居世界前1%的研究作者、机构和论文等。当然也可对某一期刊、国家或地区等的高被引论文进行检索。本研究中对907篇施引文献进行检索,共出现了10篇高水平论文(见表5)。
表5 ESI 论文基本信息
3.6 ESI 高水平论文分析
ESI(Essential Science Indicators)即基本科学指标数据库,是由美国学术信息出版机构美国科技研究所(ISI)在2026年推出的用户跟踪学科发展趋势和衡量科研绩效的评价分析工具。其评价逻辑主要是通过SSCI、SCI 数据库中近11年来的科研成果统计为评价对象,按照被引频次的高低排出居世界前1%的研究作者、机构和论文等。当然也可对某一期刊、国家或地区等的高被引论文进行检索。本研究中对907篇施引文献进行检索,共出现了10篇高水平论文(见表5)。
表5 ESI 论文基本信息
3.6 ESI 高水平论文分析
ESI(Essential Science Indicators)即基本科学指标数据库,是由美国学术信息出版机构美国科技研究所(ISI)在2026年推出的用户跟踪学科发展趋势和衡量科研绩效的评价分析工具。其评价逻辑主要是通过SSCI、SCI 数据库中近11年来的科研成果统计为评价对象,按照被引频次的高低排出居世界前1%的研究作者、机构和论文等。当然也可对某一期刊、国家或地区等的高被引论文进行检索。本研究中对907篇施引文献进行检索,共出现了10篇高水平论文(见表5)。
表5 ESI 论文基本信息
续表
续表
续表
从ESI 收录的高水平论文的发表时间来看,集中在2006—2026年这6年中,ESI 高水平论文在这6年中的发布数量如表6所示。一般来讲,发文时间越早,被引次数越高,因而发文数量最多的两年2026年和2026年是正常的分布规律。从所有ESI 高水平论文的被引情况分析,可以了解论文的受关注程度。被引次数越高,该ESI 高水平论文的受关注度也越高。当然如前分析,越早发表的论文在被引次数上较占优势。如表5所示,被引次数最高的论文名称是 “Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities:An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories”,被引次数高达447次。从这10篇ESI 高水平论文的被引次数区间分布来看,被引次数在400次以上的论文有1篇,被引次数在300次以上的论文有1篇,被引次数在100次以上有5篇,被引次数在100次以下的有3篇。可见,越是优秀的论文,数量越是少,这也符合布拉德福定律的分布规律。
表6 ESI 高水平论文发文时间分布
从ESI 收录的高水平论文的发表时间来看,集中在2006—2026年这6年中,ESI 高水平论文在这6年中的发布数量如表6所示。一般来讲,发文时间越早,被引次数越高,因而发文数量最多的两年2026年和2026年是正常的分布规律。从所有ESI 高水平论文的被引情况分析,可以了解论文的受关注程度。被引次数越高,该ESI 高水平论文的受关注度也越高。当然如前分析,越早发表的论文在被引次数上较占优势。如表5所示,被引次数最高的论文名称是 “Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities:An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories”,被引次数高达447次。从这10篇ESI 高水平论文的被引次数区间分布来看,被引次数在400次以上的论文有1篇,被引次数在300次以上的论文有1篇,被引次数在100次以上有5篇,被引次数在100次以下的有3篇。可见,越是优秀的论文,数量越是少,这也符合布拉德福定律的分布规律。
表6 ESI 高水平论文发文时间分布
从ESI 收录的高水平论文的发表时间来看,集中在2006—2026年这6年中,ESI 高水平论文在这6年中的发布数量如表6所示。一般来讲,发文时间越早,被引次数越高,因而发文数量最多的两年2026年和2026年是正常的分布规律。从所有ESI 高水平论文的被引情况分析,可以了解论文的受关注程度。被引次数越高,该ESI 高水平论文的受关注度也越高。当然如前分析,越早发表的论文在被引次数上较占优势。如表5所示,被引次数最高的论文名称是 “Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities:An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories”,被引次数高达447次。从这10篇ESI 高水平论文的被引次数区间分布来看,被引次数在400次以上的论文有1篇,被引次数在300次以上的论文有1篇,被引次数在100次以上有5篇,被引次数在100次以下的有3篇。可见,越是优秀的论文,数量越是少,这也符合布拉德福定律的分布规律。
表6 ESI 高水平论文发文时间分布
另外,从ESI 高水平论文被引次数的年度分布可以分析该研究领域研究热度的变化。如图2所示,这10篇ESI 高水平论文的年被引次数呈逐年增长趋势(因数据采集时间为2026年8月29日,所以2026年数据小于去年,但可推测整个年度的被引次数会呈继续增长态势)。这表明信息系统模型研究领域的热度持续不减,得到了相关学者的重视,研究成果也在不断增长。
另外,从ESI 高水平论文被引次数的年度分布可以分析该研究领域研究热度的变化。如图2所示,这10篇ESI 高水平论文的年被引次数呈逐年增长趋势(因数据采集时间为2026年8月29日,所以2026年数据小于去年,但可推测整个年度的被引次数会呈继续增长态势)。这表明信息系统模型研究领域的热度持续不减,得到了相关学者的重视,研究成果也在不断增长。
另外,从ESI 高水平论文被引次数的年度分布可以分析该研究领域研究热度的变化。如图2所示,这10篇ESI 高水平论文的年被引次数呈逐年增长趋势(因数据采集时间为2026年8月29日,所以2026年数据小于去年,但可推测整个年度的被引次数会呈继续增长态势)。这表明信息系统模型研究领域的热度持续不减,得到了相关学者的重视,研究成果也在不断增长。
图2 ESI 高水平论文的年被引次数分布
这10篇ESI 高水平论文中有些是对信息系统成功模型及变量纬度的探讨,还有些则是对现实中具体问题的分析。前者如Gregor从信息系统理论研究的目标视角出发,总结出信息系统理论的五种类型,分别为:用于分析(analysis)、用于解释(explanation)、用于预测(prediction)、用于解释和预测(explanation and prediction)及用于设计和执行(design and action)[32]。Jones 和Straub 则针对信息系统成功影响变量之一的系统使用变量进行了研究,提出系统使用虽在D&M 模型中多次强调,但却没有具体的概念。因此,他们通过定义和选择两阶段研究来明确系统使用的概念、基本假设和功能等[33]。Venkatesh 等对组织员工使用新信息系统的行为进行研究,提出评估系统使用中的3个关键因素,分别是持续时间、频率和强度,并进一步探讨了员工行为意愿、有利条件和行为期望与评估系统使用三要素间的关系[34]。Petter 等则对D&M 模型相关的实证研究进行梳理和总结,分别对个人和组织视角下信息系统成功模型的应用进行研究[35]。不同的学者对信息系统及信息系统成功的研究,特别是在不同的环境下,可能会提出不同的影响变量,如Benbasat 和Barki 指出了信息系统研究领域对TAM 模型的过分关注,且很多研究在不同环境下将TAM 模型衍生出了多个变量,使得TAM 理论混乱,不利于信息系统理论体系的形成[36]。
对现实中具体问题的分析,如在医疗领域中,对个人健康档案[37]、医疗保健[38]的研究,物流供应链中买家与供应商之间的信息流研究[39],教育领域中“主观任务价值”视角下的在线学习持续意愿研究[40]。此外还有些交叉领域的研究,如在虚拟社区中针对知识共享影响因素的探讨[41]。
4 信息系统成功模型应用研究进展
4.1 信息系统成功模型演化
4.1.1 早期信息系统成功研究
以时间轴为分类标准,本文将D&M 信息系统成功模型的研究主要分为三个阶段,第一阶段为D&M(1992)模型提出前的研究,其中最具代表性的包括Shannon-Weaver 模型、Mason 关于信息影响分层研究以及2026年第一届信息系统国际会议(ICIS)提出信息系统中变量研究的重要性。
在Shannon-Weaver 模型中,他们将信息分为三层,分别是技术层、语义层和效用层[2]。技术层描述的是信息系统生产信息的有效性和准确性;语义层描述的则是信息系统传达的信息是否与预设的一致;效用层则描述了信息系统的使用对于个人和组织的影响。
Mason 则针对信息系统的输出提出了一个评估框架,将信息系统输出分为技术层输出(technical level output)、语义层输出(semantic level output)、功能层输出(functional output)和影响或实用层输出(influence or pragmatic level output)[3]。
还有些学者对信息系统影响因素进行了探讨,如Zani 在《管理信息系统蓝图》 (The blueprint of MIS)中提出的“The key success variables”,探讨了什么是公司管理者决定使用信息系统的关键要素[43]。Rockart 针对企业管理中有效信息的获取和企业效率提高提出了关键成功要素(Critical success factors,CSF),通过关键成功要素法的应用,管理者可以明确管理方向,得出关键成功要素,明确所需的信息,从而限制搜集不必要的数据[43]。Zumd 将影响MIS 成功的要素分为三类,分别是用户性能(user performance)、信息系统使用(MIS usage)和用户满意(user satisfaction)[44]。Ives 和Olson 将MIS 的输出结果变量分为两类,分别是系统质量(system quality)和系统接受(system acceptance)。系统接受主要是指系统使用、系统对用户行为的影响和信息满意等[45]。
直到2026年第一届信息系统国际会议(ICIS)上,明确提出了信息系统研究中一个重要的议题即对影响信息系统的独立变量的研究,Peters 指出只有明确信息系统成功开发和应用的关键变量,才能更好地维护和优化信息系统[46]。
4.1.2 D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型
根据以上研究发现,不同的学者对信息系统研究选择的切入点不尽相同,对于信息系统成功评估也没有统一的框架和标准。在这种情况下,Delone 和McLean 在对2026年到2026年间关于MIS 的论文进行研究的基础上,将信息系统成功相关影响因素的研究进行梳理,于2026年首次提出了信息系统成功模型——D&M 模型(见图3)。在模型中,他们将多种影响信息系统成功的因素通过归纳分为六类,分别是系统质量、信息质量、系统使用、用户满意、个人影响和组织影响,这六个要素彼此间没有优先级,共同影响着信息系统成功[47]。系统质量主要是评估信息系统自身运行的过程,其一般通过易用性、可靠性、功能性、可移植性、灵活性、数据质量、整合性等指标体现;信息质量则用来评估信息系统输出信息的质量,主要通过信息的准确性、完整性、时效性、持续性和相关等指标体现;系统使用则是信息系统成功中最常用的评估要素之一;用户满意是指用户在使用信息系统后的真实感受和满意程度,这也是用户决定是否使用该信息系统的重要影响要素。此前,一些学者曾尝试通过多维度的方法来评估用户满意,如Swanson 使用16个指标来分解用户满意[48],Pearson 则开发了36维度的用户满意评估指标[49]。当然用户满意中的“用户”具体所指也是信息系统成功中需要进一步研究的。个人影响主要表现在个人在使用信息系统后的行为变化,由于个人影响与个人绩效行为相关,因此,在影响信息系统成功多个要素中,个人影响可能是最难去定义的,当然最为直接的影响主要表现为提高个人决策效率。组织影响即信息系统使用对组织绩效的影响,由于个人影响难以定义和量化,而多个个人绩效表现直接影响着组织表现,因此,一些学者直接对信息系统使用对组织的影响进行了研究,如Chismar 和Kriebel 提出评估信息系统使用与组织销售额和投资回报率的影响[50]。随着科学技术的进步,信息系统功能呈现多样化和综合性,信息系统成功对于组织的影响可能更易观察和具化,未来,这也是组织影响因素在信息系统成功研究中值得探讨的内容。
图2 ESI 高水平论文的年被引次数分布
这10篇ESI 高水平论文中有些是对信息系统成功模型及变量纬度的探讨,还有些则是对现实中具体问题的分析。前者如Gregor从信息系统理论研究的目标视角出发,总结出信息系统理论的五种类型,分别为:用于分析(analysis)、用于解释(explanation)、用于预测(prediction)、用于解释和预测(explanation and prediction)及用于设计和执行(design and action)[32]。Jones 和Straub 则针对信息系统成功影响变量之一的系统使用变量进行了研究,提出系统使用虽在D&M 模型中多次强调,但却没有具体的概念。因此,他们通过定义和选择两阶段研究来明确系统使用的概念、基本假设和功能等[33]。Venkatesh 等对组织员工使用新信息系统的行为进行研究,提出评估系统使用中的3个关键因素,分别是持续时间、频率和强度,并进一步探讨了员工行为意愿、有利条件和行为期望与评估系统使用三要素间的关系[34]。Petter 等则对D&M 模型相关的实证研究进行梳理和总结,分别对个人和组织视角下信息系统成功模型的应用进行研究[35]。不同的学者对信息系统及信息系统成功的研究,特别是在不同的环境下,可能会提出不同的影响变量,如Benbasat 和Barki 指出了信息系统研究领域对TAM 模型的过分关注,且很多研究在不同环境下将TAM 模型衍生出了多个变量,使得TAM 理论混乱,不利于信息系统理论体系的形成[36]。
对现实中具体问题的分析,如在医疗领域中,对个人健康档案[37]、医疗保健[38]的研究,物流供应链中买家与供应商之间的信息流研究[39],教育领域中“主观任务价值”视角下的在线学习持续意愿研究[40]。此外还有些交叉领域的研究,如在虚拟社区中针对知识共享影响因素的探讨[41]。
4 信息系统成功模型应用研究进展
4.1 信息系统成功模型演化
4.1.1 早期信息系统成功研究
以时间轴为分类标准,本文将D&M 信息系统成功模型的研究主要分为三个阶段,第一阶段为D&M(1992)模型提出前的研究,其中最具代表性的包括Shannon-Weaver 模型、Mason 关于信息影响分层研究以及2026年第一届信息系统国际会议(ICIS)提出信息系统中变量研究的重要性。
在Shannon-Weaver 模型中,他们将信息分为三层,分别是技术层、语义层和效用层[2]。技术层描述的是信息系统生产信息的有效性和准确性;语义层描述的则是信息系统传达的信息是否与预设的一致;效用层则描述了信息系统的使用对于个人和组织的影响。
Mason 则针对信息系统的输出提出了一个评估框架,将信息系统输出分为技术层输出(technical level output)、语义层输出(semantic level output)、功能层输出(functional output)和影响或实用层输出(influence or pragmatic level output)[3]。
还有些学者对信息系统影响因素进行了探讨,如Zani 在《管理信息系统蓝图》 (The blueprint of MIS)中提出的“The key success variables”,探讨了什么是公司管理者决定使用信息系统的关键要素[43]。Rockart 针对企业管理中有效信息的获取和企业效率提高提出了关键成功要素(Critical success factors,CSF),通过关键成功要素法的应用,管理者可以明确管理方向,得出关键成功要素,明确所需的信息,从而限制搜集不必要的数据[43]。Zumd 将影响MIS 成功的要素分为三类,分别是用户性能(user performance)、信息系统使用(MIS usage)和用户满意(user satisfaction)[44]。Ives 和Olson 将MIS 的输出结果变量分为两类,分别是系统质量(system quality)和系统接受(system acceptance)。系统接受主要是指系统使用、系统对用户行为的影响和信息满意等[45]。
直到2026年第一届信息系统国际会议(ICIS)上,明确提出了信息系统研究中一个重要的议题即对影响信息系统的独立变量的研究,Peters 指出只有明确信息系统成功开发和应用的关键变量,才能更好地维护和优化信息系统[46]。
4.1.2 D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型
根据以上研究发现,不同的学者对信息系统研究选择的切入点不尽相同,对于信息系统成功评估也没有统一的框架和标准。在这种情况下,Delone 和McLean 在对2026年到2026年间关于MIS 的论文进行研究的基础上,将信息系统成功相关影响因素的研究进行梳理,于2026年首次提出了信息系统成功模型——D&M 模型(见图3)。在模型中,他们将多种影响信息系统成功的因素通过归纳分为六类,分别是系统质量、信息质量、系统使用、用户满意、个人影响和组织影响,这六个要素彼此间没有优先级,共同影响着信息系统成功[47]。系统质量主要是评估信息系统自身运行的过程,其一般通过易用性、可靠性、功能性、可移植性、灵活性、数据质量、整合性等指标体现;信息质量则用来评估信息系统输出信息的质量,主要通过信息的准确性、完整性、时效性、持续性和相关等指标体现;系统使用则是信息系统成功中最常用的评估要素之一;用户满意是指用户在使用信息系统后的真实感受和满意程度,这也是用户决定是否使用该信息系统的重要影响要素。此前,一些学者曾尝试通过多维度的方法来评估用户满意,如Swanson 使用16个指标来分解用户满意[48],Pearson 则开发了36维度的用户满意评估指标[49]。当然用户满意中的“用户”具体所指也是信息系统成功中需要进一步研究的。个人影响主要表现在个人在使用信息系统后的行为变化,由于个人影响与个人绩效行为相关,因此,在影响信息系统成功多个要素中,个人影响可能是最难去定义的,当然最为直接的影响主要表现为提高个人决策效率。组织影响即信息系统使用对组织绩效的影响,由于个人影响难以定义和量化,而多个个人绩效表现直接影响着组织表现,因此,一些学者直接对信息系统使用对组织的影响进行了研究,如Chismar 和Kriebel 提出评估信息系统使用与组织销售额和投资回报率的影响[50]。随着科学技术的进步,信息系统功能呈现多样化和综合性,信息系统成功对于组织的影响可能更易观察和具化,未来,这也是组织影响因素在信息系统成功研究中值得探讨的内容。
图2 ESI 高水平论文的年被引次数分布
这10篇ESI 高水平论文中有些是对信息系统成功模型及变量纬度的探讨,还有些则是对现实中具体问题的分析。前者如Gregor从信息系统理论研究的目标视角出发,总结出信息系统理论的五种类型,分别为:用于分析(analysis)、用于解释(explanation)、用于预测(prediction)、用于解释和预测(explanation and prediction)及用于设计和执行(design and action)[32]。Jones 和Straub 则针对信息系统成功影响变量之一的系统使用变量进行了研究,提出系统使用虽在D&M 模型中多次强调,但却没有具体的概念。因此,他们通过定义和选择两阶段研究来明确系统使用的概念、基本假设和功能等[33]。Venkatesh 等对组织员工使用新信息系统的行为进行研究,提出评估系统使用中的3个关键因素,分别是持续时间、频率和强度,并进一步探讨了员工行为意愿、有利条件和行为期望与评估系统使用三要素间的关系[34]。Petter 等则对D&M 模型相关的实证研究进行梳理和总结,分别对个人和组织视角下信息系统成功模型的应用进行研究[35]。不同的学者对信息系统及信息系统成功的研究,特别是在不同的环境下,可能会提出不同的影响变量,如Benbasat 和Barki 指出了信息系统研究领域对TAM 模型的过分关注,且很多研究在不同环境下将TAM 模型衍生出了多个变量,使得TAM 理论混乱,不利于信息系统理论体系的形成[36]。
对现实中具体问题的分析,如在医疗领域中,对个人健康档案[37]、医疗保健[38]的研究,物流供应链中买家与供应商之间的信息流研究[39],教育领域中“主观任务价值”视角下的在线学习持续意愿研究[40]。此外还有些交叉领域的研究,如在虚拟社区中针对知识共享影响因素的探讨[41]。
4 信息系统成功模型应用研究进展
4.1 信息系统成功模型演化
4.1.1 早期信息系统成功研究
以时间轴为分类标准,本文将D&M 信息系统成功模型的研究主要分为三个阶段,第一阶段为D&M(1992)模型提出前的研究,其中最具代表性的包括Shannon-Weaver 模型、Mason 关于信息影响分层研究以及2026年第一届信息系统国际会议(ICIS)提出信息系统中变量研究的重要性。
在Shannon-Weaver 模型中,他们将信息分为三层,分别是技术层、语义层和效用层[2]。技术层描述的是信息系统生产信息的有效性和准确性;语义层描述的则是信息系统传达的信息是否与预设的一致;效用层则描述了信息系统的使用对于个人和组织的影响。
Mason 则针对信息系统的输出提出了一个评估框架,将信息系统输出分为技术层输出(technical level output)、语义层输出(semantic level output)、功能层输出(functional output)和影响或实用层输出(influence or pragmatic level output)[3]。
还有些学者对信息系统影响因素进行了探讨,如Zani 在《管理信息系统蓝图》 (The blueprint of MIS)中提出的“The key success variables”,探讨了什么是公司管理者决定使用信息系统的关键要素[43]。Rockart 针对企业管理中有效信息的获取和企业效率提高提出了关键成功要素(Critical success factors,CSF),通过关键成功要素法的应用,管理者可以明确管理方向,得出关键成功要素,明确所需的信息,从而限制搜集不必要的数据[43]。Zumd 将影响MIS 成功的要素分为三类,分别是用户性能(user performance)、信息系统使用(MIS usage)和用户满意(user satisfaction)[44]。Ives 和Olson 将MIS 的输出结果变量分为两类,分别是系统质量(system quality)和系统接受(system acceptance)。系统接受主要是指系统使用、系统对用户行为的影响和信息满意等[45]。
直到2026年第一届信息系统国际会议(ICIS)上,明确提出了信息系统研究中一个重要的议题即对影响信息系统的独立变量的研究,Peters 指出只有明确信息系统成功开发和应用的关键变量,才能更好地维护和优化信息系统[46]。
4.1.2 D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型
根据以上研究发现,不同的学者对信息系统研究选择的切入点不尽相同,对于信息系统成功评估也没有统一的框架和标准。在这种情况下,Delone 和McLean 在对2026年到2026年间关于MIS 的论文进行研究的基础上,将信息系统成功相关影响因素的研究进行梳理,于2026年首次提出了信息系统成功模型——D&M 模型(见图3)。在模型中,他们将多种影响信息系统成功的因素通过归纳分为六类,分别是系统质量、信息质量、系统使用、用户满意、个人影响和组织影响,这六个要素彼此间没有优先级,共同影响着信息系统成功[47]。系统质量主要是评估信息系统自身运行的过程,其一般通过易用性、可靠性、功能性、可移植性、灵活性、数据质量、整合性等指标体现;信息质量则用来评估信息系统输出信息的质量,主要通过信息的准确性、完整性、时效性、持续性和相关等指标体现;系统使用则是信息系统成功中最常用的评估要素之一;用户满意是指用户在使用信息系统后的真实感受和满意程度,这也是用户决定是否使用该信息系统的重要影响要素。此前,一些学者曾尝试通过多维度的方法来评估用户满意,如Swanson 使用16个指标来分解用户满意[48],Pearson 则开发了36维度的用户满意评估指标[49]。当然用户满意中的“用户”具体所指也是信息系统成功中需要进一步研究的。个人影响主要表现在个人在使用信息系统后的行为变化,由于个人影响与个人绩效行为相关,因此,在影响信息系统成功多个要素中,个人影响可能是最难去定义的,当然最为直接的影响主要表现为提高个人决策效率。组织影响即信息系统使用对组织绩效的影响,由于个人影响难以定义和量化,而多个个人绩效表现直接影响着组织表现,因此,一些学者直接对信息系统使用对组织的影响进行了研究,如Chismar 和Kriebel 提出评估信息系统使用与组织销售额和投资回报率的影响[50]。随着科学技术的进步,信息系统功能呈现多样化和综合性,信息系统成功对于组织的影响可能更易观察和具化,未来,这也是组织影响因素在信息系统成功研究中值得探讨的内容。
图3 D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型
考虑到信息系统成功模型在现实中的应用,模型中的影响因素必须足够完整和简洁。所谓完整是能够全面地囊括影响信息系统成功的多种因素,如信息质量、系统质量和用户满意等;所谓简洁则是对影响因素的提炼必须合理,在现实应用中可以找到合理归类潜变量。因此,在D&M 信息系统成功模型中,共提出了六类影响因素,并提出了在选择影响信息系统成功模型影响因素的时候还应考虑到一些权变变量,如组织的战略、结构、规模和环境等,还有诸如个体性格和技术应用等[47]。
4.1.3 D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型
由于在D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中,并没有通过实证研究来验证模型中关系的假设及各要素间正向影响关系的强弱,且没有对这些权变变量进行更深入的探讨。因此,在2026年Delone和Mclean 提出了“升级版”的信息系统成功模型[51](见图4)。D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型主要是在原有模型的基础上更注重模型的应用效果、有效性和面临的挑战等。事实上,在1992—2026年已有很多学者以D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型为基础研究信息系统成功模型,并进行了相关实证研究,如Seddon 和Kiew对使用过大学会计系统的104位用户进行研究发现,系统质量与用户使用和个人影响间、信息质量与用户满意和个人影响间都存在显著性影响关系,这与D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中的假设一致[52]。Rai 等则通过实证研究得出,D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中的所有路径系数都呈显著性,证明了D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型的科学性[53]。Delone 和Mclean 也对利用D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型进行的相关实证研究进行了归纳,如验证系统使用和个人影响间显著性关系的研究[54][55][56][57],系统质量与个人影响、信息质量与个人影响间显著性关系的研究[58][59][60][61]用来佐证其科学性。但也有些学者在研究中对D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型提出了异议,如Seddon 指出系统使用不应归纳到信息系统成功中,他强调使用作为一种行为应作为一个过程而不是因果关系应用到模型中[62]。但Delone 和Mclean 依然认为系统使用应属于信息系统成功影响因素之一,只有用户使用了信息系统,才会产生个人影响和利益。当然这种使用可以理解为多维因素,如Young 和Benamati 认为对电子商务系统的使用应包括信息使用和客户服务使用等[63]。
在D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型中(见图4),Delone 和Mclean 将质量维度分为信息质量、系统质量和服务质量三个变量,这三个变量又分别影响着用户使用和用户满意。在D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中并没有对系统使用进行明确解释,是自愿还是非自愿使用,是知情还是不知情情况下的使用等,都没有明确的说明。因此在D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型中,Delone 和Mclean将系统使用明确为使用意愿,该变量不仅代表着一个行为也说明了用户的态度。系统使用变量的转变也有助于其在实践评估中的应用。用户使用系统并满意之后自然会产生纯收益,这对系统使用者和赞助商都是有积极作用的,这一积极效果又将促进用户继续使用该信息系统,形成一个良性的循环。如果“净收益”(net benefits)结果不够理想,可能会导致用户减少甚至是拒绝使用该信息系统,因此明确在不同的应用领域中的信息系统利益相关者对于信息系统成功评估研究者来说十分重要。
图3 D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型
考虑到信息系统成功模型在现实中的应用,模型中的影响因素必须足够完整和简洁。所谓完整是能够全面地囊括影响信息系统成功的多种因素,如信息质量、系统质量和用户满意等;所谓简洁则是对影响因素的提炼必须合理,在现实应用中可以找到合理归类潜变量。因此,在D&M 信息系统成功模型中,共提出了六类影响因素,并提出了在选择影响信息系统成功模型影响因素的时候还应考虑到一些权变变量,如组织的战略、结构、规模和环境等,还有诸如个体性格和技术应用等[47]。
4.1.3 D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型
图3 D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型
考虑到信息系统成功模型在现实中的应用,模型中的影响因素必须足够完整和简洁。所谓完整是能够全面地囊括影响信息系统成功的多种因素,如信息质量、系统质量和用户满意等;所谓简洁则是对影响因素的提炼必须合理,在现实应用中可以找到合理归类潜变量。因此,在D&M 信息系统成功模型中,共提出了六类影响因素,并提出了在选择影响信息系统成功模型影响因素的时候还应考虑到一些权变变量,如组织的战略、结构、规模和环境等,还有诸如个体性格和技术应用等[47]。
4.1.3 D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型
由于在D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中,并没有通过实证研究来验证模型中关系的假设及各要素间正向影响关系的强弱,且没有对这些权变变量进行更深入的探讨。因此,在2026年Delone和Mclean 提出了“升级版”的信息系统成功模型[51](见图4)。D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型主要是在原有模型的基础上更注重模型的应用效果、有效性和面临的挑战等。事实上,在1992—2026年已有很多学者以D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型为基础研究信息系统成功模型,并进行了相关实证研究,如Seddon 和Kiew对使用过大学会计系统的104位用户进行研究发现,系统质量与用户使用和个人影响间、信息质量与用户满意和个人影响间都存在显著性影响关系,这与D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中的假设一致[52]。Rai 等则通过实证研究得出,D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中的所有路径系数都呈显著性,证明了D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型的科学性[53]。Delone 和Mclean 也对利用D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型进行的相关实证研究进行了归纳,如验证系统使用和个人影响间显著性关系的研究[54][55][56][57],系统质量与个人影响、信息质量与个人影响间显著性关系的研究[58][59][60][61]用来佐证其科学性。但也有些学者在研究中对D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型提出了异议,如Seddon 指出系统使用不应归纳到信息系统成功中,他强调使用作为一种行为应作为一个过程而不是因果关系应用到模型中[62]。但Delone 和Mclean 依然认为系统使用应属于信息系统成功影响因素之一,只有用户使用了信息系统,才会产生个人影响和利益。当然这种使用可以理解为多维因素,如Young 和Benamati 认为对电子商务系统的使用应包括信息使用和客户服务使用等[63]。
在D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型中(见图4),Delone 和Mclean 将质量维度分为信息质量、系统质量和服务质量三个变量,这三个变量又分别影响着用户使用和用户满意。在D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中并没有对系统使用进行明确解释,是自愿还是非自愿使用,是知情还是不知情情况下的使用等,都没有明确的说明。因此在D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型中,Delone 和Mclean将系统使用明确为使用意愿,该变量不仅代表着一个行为也说明了用户的态度。系统使用变量的转变也有助于其在实践评估中的应用。用户使用系统并满意之后自然会产生纯收益,这对系统使用者和赞助商都是有积极作用的,这一积极效果又将促进用户继续使用该信息系统,形成一个良性的循环。如果“净收益”(net benefits)结果不够理想,可能会导致用户减少甚至是拒绝使用该信息系统,因此明确在不同的应用领域中的信息系统利益相关者对于信息系统成功评估研究者来说十分重要。
由于在D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中,并没有通过实证研究来验证模型中关系的假设及各要素间正向影响关系的强弱,且没有对这些权变变量进行更深入的探讨。因此,在2026年Delone和Mclean 提出了“升级版”的信息系统成功模型[51](见图4)。D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型主要是在原有模型的基础上更注重模型的应用效果、有效性和面临的挑战等。事实上,在1992—2026年已有很多学者以D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型为基础研究信息系统成功模型,并进行了相关实证研究,如Seddon 和Kiew对使用过大学会计系统的104位用户进行研究发现,系统质量与用户使用和个人影响间、信息质量与用户满意和个人影响间都存在显著性影响关系,这与D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中的假设一致[52]。Rai 等则通过实证研究得出,D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中的所有路径系数都呈显著性,证明了D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型的科学性[53]。Delone 和Mclean 也对利用D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型进行的相关实证研究进行了归纳,如验证系统使用和个人影响间显著性关系的研究[54][55][56][57],系统质量与个人影响、信息质量与个人影响间显著性关系的研究[58][59][60][61]用来佐证其科学性。但也有些学者在研究中对D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型提出了异议,如Seddon 指出系统使用不应归纳到信息系统成功中,他强调使用作为一种行为应作为一个过程而不是因果关系应用到模型中[62]。但Delone 和Mclean 依然认为系统使用应属于信息系统成功影响因素之一,只有用户使用了信息系统,才会产生个人影响和利益。当然这种使用可以理解为多维因素,如Young 和Benamati 认为对电子商务系统的使用应包括信息使用和客户服务使用等[63]。
在D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型中(见图4),Delone 和Mclean 将质量维度分为信息质量、系统质量和服务质量三个变量,这三个变量又分别影响着用户使用和用户满意。在D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型中并没有对系统使用进行明确解释,是自愿还是非自愿使用,是知情还是不知情情况下的使用等,都没有明确的说明。因此在D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型中,Delone 和Mclean将系统使用明确为使用意愿,该变量不仅代表着一个行为也说明了用户的态度。系统使用变量的转变也有助于其在实践评估中的应用。用户使用系统并满意之后自然会产生纯收益,这对系统使用者和赞助商都是有积极作用的,这一积极效果又将促进用户继续使用该信息系统,形成一个良性的循环。如果“净收益”(net benefits)结果不够理想,可能会导致用户减少甚至是拒绝使用该信息系统,因此明确在不同的应用领域中的信息系统利益相关者对于信息系统成功评估研究者来说十分重要。
图4 D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型
因此,Delone 和Mclean 针对电子商务环境下的纯收益提出了一些具体的评估指标,如成本节约、扩大市场、销售增量、降低搜索成本等,对于6个影响变量在电子商务环境下也有具体的解释[64],如电子商务环境下的系统质量可通过易用性、可用性、可靠性、适用性、功能性、响应时间、灵活性、数据质量等指标来评估;信息质量则应具有个性化、完整性、相关性、易于用户理解等特性,并能保证用户购买过程的安全;对服务质量来说,不管提供服务质量的是一个新的组织部门还是网络服务提供商,最为重要的都是提供优质的服务来提高用户数量和销售额;使用则可通过网页访问、网址点击、信息检索和交易执行等方面来体现;用户满意则包括用户使用该系统的整个过程,如信息检索、购买、付款和售后服务等环节;最后,纯收益是对于电子商务环境下,信息系统应用到各个环节用户利益的评估,如客户、供应商、雇员、组织者、市场、行业、环境甚至社会。
经过十年的发展,D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型除了对D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型进行了一些调整和完善,还希望D&M 信息系统成功模型能够更好地应用到不同环境中。虽然在这过程中还有些学者提出了其他信息系统成功模型,如上文提到的由Seddon 提出的信息系统成功模型(见图5),还有Jennex 等提出的OMIS 成功模型[65]等。但这些模型依然是以D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型为基础的演化或延生。
图4 D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型
因此,Delone 和Mclean 针对电子商务环境下的纯收益提出了一些具体的评估指标,如成本节约、扩大市场、销售增量、降低搜索成本等,对于6个影响变量在电子商务环境下也有具体的解释[64],如电子商务环境下的系统质量可通过易用性、可用性、可靠性、适用性、功能性、响应时间、灵活性、数据质量等指标来评估;信息质量则应具有个性化、完整性、相关性、易于用户理解等特性,并能保证用户购买过程的安全;对服务质量来说,不管提供服务质量的是一个新的组织部门还是网络服务提供商,最为重要的都是提供优质的服务来提高用户数量和销售额;使用则可通过网页访问、网址点击、信息检索和交易执行等方面来体现;用户满意则包括用户使用该系统的整个过程,如信息检索、购买、付款和售后服务等环节;最后,纯收益是对于电子商务环境下,信息系统应用到各个环节用户利益的评估,如客户、供应商、雇员、组织者、市场、行业、环境甚至社会。
经过十年的发展,D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型除了对D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型进行了一些调整和完善,还希望D&M 信息系统成功模型能够更好地应用到不同环境中。虽然在这过程中还有些学者提出了其他信息系统成功模型,如上文提到的由Seddon 提出的信息系统成功模型(见图5),还有Jennex 等提出的OMIS 成功模型[65]等。但这些模型依然是以D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型为基础的演化或延生。
图4 D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型
因此,Delone 和Mclean 针对电子商务环境下的纯收益提出了一些具体的评估指标,如成本节约、扩大市场、销售增量、降低搜索成本等,对于6个影响变量在电子商务环境下也有具体的解释[64],如电子商务环境下的系统质量可通过易用性、可用性、可靠性、适用性、功能性、响应时间、灵活性、数据质量等指标来评估;信息质量则应具有个性化、完整性、相关性、易于用户理解等特性,并能保证用户购买过程的安全;对服务质量来说,不管提供服务质量的是一个新的组织部门还是网络服务提供商,最为重要的都是提供优质的服务来提高用户数量和销售额;使用则可通过网页访问、网址点击、信息检索和交易执行等方面来体现;用户满意则包括用户使用该系统的整个过程,如信息检索、购买、付款和售后服务等环节;最后,纯收益是对于电子商务环境下,信息系统应用到各个环节用户利益的评估,如客户、供应商、雇员、组织者、市场、行业、环境甚至社会。
经过十年的发展,D&M(2003)信息系统成功模型除了对D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型进行了一些调整和完善,还希望D&M 信息系统成功模型能够更好地应用到不同环境中。虽然在这过程中还有些学者提出了其他信息系统成功模型,如上文提到的由Seddon 提出的信息系统成功模型(见图5),还有Jennex 等提出的OMIS 成功模型[65]等。但这些模型依然是以D&M(1992)信息系统成功模型为基础的演化或延生。
图5 Seddon 信息系统成功模型[62]
通过对信息系统成功模型的研究进行梳理可知,D&M 信息系统成功模型在信息系统成功研究中占有重要地位,并被越来越多的学者接受去分析具体的问题,如Yoon 和Occeña 通过实证研究分析了C2C(consumer-to-consumer)市场中影响用户信任的影响因素,并从性别和年龄等指标探讨了用户感知差异[66]。Ghobakhloo 则对B2B 电子商务信息系统成功进行了研究,他们从供应链网络的视角出发,通过对122个供应链单位的实证数据调研分析发现,除系统质量、信息质量等变量,电子商务平台的准备状态(readiness)即经济和技术资源的可用性与电子商务平台的成功也具有显著性的影响关系[67]。Beck 等则从组织机构的社交媒体中知识交换的知识获取者和知识贡献者为什么以及如何进行知识共享行为进行探讨[68]。Tsai 等以台湾一些公司为实证研究对象,探讨了在企业资源计划系统中内部审计部门的绩效问题[69]。
4.2 基于关键词词频分析的研究热点
通过将施引文献出刊年份限制在2013—2026年,结果共得到347篇施引文献。针对这347篇文献的数据进行搜集统计,抽取关键词并作词频分析。
首先,去除没有特定指代意义的关键词,如 “research,technology,study”等。其次,由于是以“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”作为标题关键词进行的检索,施引文献中信息系统成功模型探讨不可避免地会出现D&M 模型中的相关内容,如D&M 模型中的变量影响用户满意、服务质量、信息质量、系统质量等,因此,类似用户满意、服务质量等关键词肯定会是高频词汇,如 “satisfaction/ User Satisfaction”共出现45次,“service quality/ information quality system quality”共出现48次,因此,在对关键词词频统计的过程中,人工将“user satisfaction”“ service quality”“information quality”“system quality”等高频词汇剔除。最后,将关键词及关键词缩写形式进行合并,如“E-Commerce”和 “Electronic commerce” “enterprise resource planning”和“ERP”,对相同意思的不同表达方式,或同属一类研究范围关键词取较大概念范围词进行概括合并,如“online shopping”归为“Electronic Commerce”一类并合并。对高频关键词进行了重新编辑,得到详细高频词汇统计及归类(见表7)。
表7 关键词词频统计
图5 Seddon 信息系统成功模型[62]
通过对信息系统成功模型的研究进行梳理可知,D&M 信息系统成功模型在信息系统成功研究中占有重要地位,并被越来越多的学者接受去分析具体的问题,如Yoon 和Occeña 通过实证研究分析了C2C(consumer-to-consumer)市场中影响用户信任的影响因素,并从性别和年龄等指标探讨了用户感知差异[66]。Ghobakhloo 则对B2B 电子商务信息系统成功进行了研究,他们从供应链网络的视角出发,通过对122个供应链单位的实证数据调研分析发现,除系统质量、信息质量等变量,电子商务平台的准备状态(readiness)即经济和技术资源的可用性与电子商务平台的成功也具有显著性的影响关系[67]。Beck 等则从组织机构的社交媒体中知识交换的知识获取者和知识贡献者为什么以及如何进行知识共享行为进行探讨[68]。Tsai 等以台湾一些公司为实证研究对象,探讨了在企业资源计划系统中内部审计部门的绩效问题[69]。
4.2 基于关键词词频分析的研究热点
通过将施引文献出刊年份限制在2013—2026年,结果共得到347篇施引文献。针对这347篇文献的数据进行搜集统计,抽取关键词并作词频分析。
首先,去除没有特定指代意义的关键词,如 “research,technology,study”等。其次,由于是以“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”作为标题关键词进行的检索,施引文献中信息系统成功模型探讨不可避免地会出现D&M 模型中的相关内容,如D&M 模型中的变量影响用户满意、服务质量、信息质量、系统质量等,因此,类似用户满意、服务质量等关键词肯定会是高频词汇,如 “satisfaction/ User Satisfaction”共出现45次,“service quality/ information quality system quality”共出现48次,因此,在对关键词词频统计的过程中,人工将“user satisfaction”“ service quality”“information quality”“system quality”等高频词汇剔除。最后,将关键词及关键词缩写形式进行合并,如“E-Commerce”和 “Electronic commerce” “enterprise resource planning”和“ERP”,对相同意思的不同表达方式,或同属一类研究范围关键词取较大概念范围词进行概括合并,如“online shopping”归为“Electronic Commerce”一类并合并。对高频关键词进行了重新编辑,得到详细高频词汇统计及归类(见表7)。
表7 关键词词频统计
图5 Seddon 信息系统成功模型[62]
通过对信息系统成功模型的研究进行梳理可知,D&M 信息系统成功模型在信息系统成功研究中占有重要地位,并被越来越多的学者接受去分析具体的问题,如Yoon 和Occeña 通过实证研究分析了C2C(consumer-to-consumer)市场中影响用户信任的影响因素,并从性别和年龄等指标探讨了用户感知差异[66]。Ghobakhloo 则对B2B 电子商务信息系统成功进行了研究,他们从供应链网络的视角出发,通过对122个供应链单位的实证数据调研分析发现,除系统质量、信息质量等变量,电子商务平台的准备状态(readiness)即经济和技术资源的可用性与电子商务平台的成功也具有显著性的影响关系[67]。Beck 等则从组织机构的社交媒体中知识交换的知识获取者和知识贡献者为什么以及如何进行知识共享行为进行探讨[68]。Tsai 等以台湾一些公司为实证研究对象,探讨了在企业资源计划系统中内部审计部门的绩效问题[69]。
4.2 基于关键词词频分析的研究热点
通过将施引文献出刊年份限制在2013—2026年,结果共得到347篇施引文献。针对这347篇文献的数据进行搜集统计,抽取关键词并作词频分析。
首先,去除没有特定指代意义的关键词,如 “research,technology,study”等。其次,由于是以“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”作为标题关键词进行的检索,施引文献中信息系统成功模型探讨不可避免地会出现D&M 模型中的相关内容,如D&M 模型中的变量影响用户满意、服务质量、信息质量、系统质量等,因此,类似用户满意、服务质量等关键词肯定会是高频词汇,如 “satisfaction/ User Satisfaction”共出现45次,“service quality/ information quality system quality”共出现48次,因此,在对关键词词频统计的过程中,人工将“user satisfaction”“ service quality”“information quality”“system quality”等高频词汇剔除。最后,将关键词及关键词缩写形式进行合并,如“E-Commerce”和 “Electronic commerce” “enterprise resource planning”和“ERP”,对相同意思的不同表达方式,或同属一类研究范围关键词取较大概念范围词进行概括合并,如“online shopping”归为“Electronic Commerce”一类并合并。对高频关键词进行了重新编辑,得到详细高频词汇统计及归类(见表7)。
表7 关键词词频统计
通过表7可见,D&M 信息系统成功模型研究的热点,主要集中在在线学习[70][71]、企业资源计划[72][73][74]、电子商务[75][76][77]、社交网络和社交媒体[102][103][104]、知识管理[78][79]和医疗健康[80][81][82[]等研究范围。这些研究对象在一定程度上反映了近年来信息系统成功模型的应用已经涉及教育、经济、政治、医疗和互联网等各个领域,进一步展现了模型具有良好的应用性。信息系统成功模型在施引文献中的实际应用主要是通过两种方式:一种主要是利用D&M 信息系统成功模型中的相关变量或概念为指导对现实中具体问题进行的研究;另一种则是D&M 信息系统成功模型与其他模型相结合或者加入其他变量探讨实际问题。下面通过实例来展示这两种形式在研究热点中的应用。
第一种应用:Lin 大多研究都是针对网络环境下的信息系统成功的分析,如通过对232名学生进行调查分析,研究结果发现,系统质量、信息质量和服务质量对于学生在线学习系统的成功都具有显著影响[83];对网络环境下通过组织间和组织内两方面来探究组织间信息系统成功的影响变量[84]。Lee 等通过实证研究台湾202位信息系统管理者对研究模型中构面进行测试,并利用结构方程技术对研究模型进行评估,研究发现,环境因素中的“交易伙伴影响”变量及组织因素中的变量对组织间系统计划成功都具有显著性影响[85]。Dwivedi 等则将信息系统成功模型应用到图书馆领域中,探讨了射频技术(radio frequency identification,RFID)在图书馆中的应用,分析了RFID 系统的信息质量、系统质量和服务质量对用户使用及用户满意的影响,研究得出,射频技术在图书馆管理与服务中是十分受欢迎的技术之一[86]。Nguyen L,Bellucci E,Nguyen L T基于信息系统成功模型,评估电子病历中信息系统的作用和偶然性因素的影响[93]。此外,还有学者将信息系统成功模型应用到其他领域的研究,如对网络环境下的电子商务[87]、电子政务[88]、虚拟社区[89][90]、移动银行[91]、知识管理[92]等领域进行了探究。
第二种应用:Wu C H,Chen S C 通过构建包含信息质量、系统质量、功能质量和社会影响的概念框架,去探索影响Facebook用户教育性使用意愿的关键因素[102]。Shareef 等利用结构方程模型的方法,将TAM 与D&M 模型的结合对台湾地区的B2C(businessto-consumer)电子商务系统用户持续使用意愿进行了研究,研究发现D&M 信息系统成功模型中的信息质量、系统质量和服务质量对用户感知有用和用户满意都具有正向的影响[93]。Wang 等则通过将D&M 信息系统成功模型与教育技术成功模型相结合,对在线博客学习系统的影响因素进行了研究,由于在线博客学习对于网络环境的特殊要求,该研究将信息质量这一变量分为内容质量和链接质量两个维度,并分别分析了它们与用户满意及系统使用的关系[94]。
另外对云计算[95]、数字鸿沟[96]、网页质量[95][97]等问题的探讨,则表明信息系统成功研究越来越具体到现实的问题中。当然,其中也出现了很多学科间交叉的研究,如Hsieh 通过将云存储云计算与医疗行业相结合,研究专业医疗团队在使用云技术的接受情况和存在偏见等[98]。My-Trinh 等则基于归因理论对在线旅游社区的用户使用意愿进行了研究,研究得出高质量的信息服务可以为用户提供良好的信息反馈,有助于提高在线旅游社区的用户粘性[99]。Liaw 和Huang 从交互环境视角下对在线学习系统的应用进行研究,对196名大学生在使用在线学习系统数月后进行问卷调查,通过实证研究发现,感知有用和感知满意等在线学习系统成功影响因素都受到交互学习环境的影响[100]。
4.3 研究趋势展望
通过对近三年(2013—2026年)施引文献的关键词词频统计和相关文献内容阅读分析后发现,D&M 信息系统成功模型研究趋势主要表现在两个方面:
趋势之一主要体现在研究方向上,在互联网领域如虚拟社区、在线学习;医疗领域如医疗健康系统、电子病历;经济领域如电子商务;政治领域如电子政务等。这些研究中有的是直接利用D&M信息系统成功模型作为理论基础对具体问题进行的分析,更多一些则是通过将D&M 信息系统成功模型与相关理论结合对实际问题的探究。无论如何,信息系统成功模型的研究在多个领域和许多实际问题中的应用趋势不可阻挡。
趋势之二体现在研究平台上,通过对2013—2026年的施引文献内容进行分析不难发现,其中以移动平台为研究对象的信息系统成功研究探讨逐渐增多[101][102][103],这与时下移动终端设备及移动终端应用的普及是相辅相成的。如Ryu 等对用户面向移动平台如Google 或Apple 提供的应用平台使用忠诚的影响因素进行的研究,通过研究发现满意是用户忠实使用某一移动平台的重要影响变量,而移动平台的软件开发水平则决定了用户的满意度,研究还发现可信度与忠诚度之间并没有直接的影响[104];Jung 则对用户在泛在学习环境中使用智能手机的满意度和绩效影响变量展开研究,这也说明了移动智能终端设备作为当下及未来用户用于学习的重要工具之一[105]。Okazaki 等学者则对移动环境下医疗监控问题进行了探究,研究发现自我效能和兼容性是用户使用移动医疗监控信息系统的重要影响变量[106]。Pu 则对移动图书馆APP 的设计和应用进行了研究[107]。
5 结 语
随着信息系统在人们生活、工作和娱乐活动中广泛的应用和渗透,信息系统成功研究已受到越来越多的学者关注。DeLone 和McLean 于2026年发表的论文“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”提出了更新的信息系统成功模型,对信息系统成功研究产生了巨大影响。本研究针对引用了该文且被SSCI 数据库收录的期刊论文,结合论文发表年代、发文作者、发文作者机构、发文国家/地区、发文领域和ESI 论文等进行了统计分析。同时,结合关键词词频统计总结出近三年来信息系统成功模型应用研究的热点。最后,通过对施引文献的内容分析,发现信息系统成功模型的应用领域和应用环境越来越广。展望未来,面对移动互联网和物联网等新环境,信息系统的成功还会不断地面临新的问题,有待国内外相关学者积极开展系统和深入的研究,推动各类信息系统在实际应用中获得成功。
参考文献
[1]Vodanovich S,Sundaram D,Myers M.Research commentarydigital natives and ubiquitous information systems [ J ].Information Systems Research,2010,21(4): 711-723.
[2]Shannon C E,Weaver W.The mathematical theory of communication [M].Urbana,IL: University of Illinois Press,1949.
[3]Mason R O.Measuring information output: A communication systems approach [J].Information & Management,1978,1(78): 219-234.
[4]DeLone W H,McLean E R.The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update [J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2003,19(4): 9-30.
[5]Hong S,Katerattanakul P,Hong S K,et al.Usage and perceived impact of data warehouses: A study in Korean financial companies[J].International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making,2006,5(2): 297-315.
[6]Lai J Y.Assessment of employees’ perceptions of service quality and satisfaction with e-business [J].International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,2006,64(9): 926-938.
[7]Wang Y S,Liao Y W.The conceptualization and measurement of m-commerce user satisfaction [ J ].Computers in Human Behavior,2007,23(1): 381-398.
[8]Lin H F.The impact of website quality dimensions on customer satisfaction in the B2C e-commerce context [J].Total Quality Management and Business Excellence,2007,18(4): 363-378.
[9]Gil-García J R,Pardo T A.E-government success factors:Mapping practical tools to theoretical foundations [J].Government Information Quarterly,2005,22(2): 187-216.
[10]Prybutok V R,Zhang X,Ryan S D.Evaluating leadership,IT quality,and net benefits in an e-government environment [J].Information & Management,2008,45(3): 143-152.
[11]Connell N A D,Young T P.Evaluating healthcare information systems through an “enterprise”perspective [J].Information &Management,2007,44(4): 433-440.
[12]Shahmoradi L,Ahmadi M,Haghani H.Determining the most important evaluation indicators of healthcare information systems(HCIS) in Iran [J].Health Information Management Journal,2007,36(1): 13-22.
[13]Ong C S,Lai J Y.Gender differences in perceptions and relationships among dominants of e-learning acceptance [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2006,22(5): 816-829.
[14]Wang Y S,Wang H Y,Shee D Y.Measuring e-learning systems success in an organizational context: Scale development and validation [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2007,23(4):1792-1808.
[15]Lin H F.Measuring online learning systems success: Applying the updated DeLone and McLean model [J].Cyberpsychology &Behavior,2007,10(6): 817-820.
[16]Barczak G,Sultan F,Hultink E J.Determinants of IT usage and new product performance[J].Journal of Product Innovation Management,2007,24(6): 600-613.
[17]Cui L,Zhang C,Zhang C,et al.Exploring IT adoption process in shanghai firms: An empirical study [J].Journal of Global Information Management,2008,16(2): 1-17.
[18]Avlonitis G J,Panagopoulos N G.Antecedents and consequences of CRM technology acceptance in the sales force [J].Industrial Marketing Management,2005,34(4): 355-368.
[19]Xue Y,Liang H,Boulton W R,et al.ERP implementation failures in China: Case studies with implications for ERP vendors[J].International Journal of Production Economics,2005,97(3): 279-295.
[20]Wu J H,Wang Y M.Measuring ERP success:The ultimate users'view [J].International Journal of Operations & Production Management,2006,26(8): 882-903.
[21]Wang E T G,Ying T C,Jiang J J,et al.Group cohesion in organizational innovation: An empirical examination of ERP implementation [ J].Information and Software Technology,2006,48(4): 235-244.
[22]Lin H Y,Hsu P Y,Ting P H.ERP systems success: An integration of IS success model and balanced scorecard [J].Journal of Research and Practice in Information Technology,2006,38(3): 215-228.
[23]Chiu C M,Hsu M H,Wang E T G.Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories [J].Decision Support Systems,2006,42(3): 1872-1888.
[24]Kulkarni U R,Ravindran S,Freeze R.A knowledge management success model: Theoretical development and empirical validation[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2006,23(3): 309-347.
[25]Petter S,DeLone W,McLean E.Measuring information systems success: Models,dimensions,measures,and interrelationships[J].European Journal of Information Systems,2008,17(3):236-263.
[26]Kulkarni U R,Ravindran S,Freeze R.A knowledge management success model: Theoretical development and empirical validation[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2006,23(3): 309-347.
[27]Wu J H,Wang Y M.Measuring KMS success: A respecification of the DeLone and McLean's model [ J].Information &Management,2006,43(6): 728-739.
[28]Ha S H,Noh M J,Choi S B.Difference in the adoption of internet open markets between transition and established market economies [J].Electronic Commerce Research,2014,14(4):531-558.
[29]Song J,Kim J,Jones D R,et al.Application discoverability and user satisfaction in mobile application stores: An environmental psychology perspective [J].Decision Support Systems,2014(59): 37-51.
[30]Flynn D,Gregory P,Makki H,et al.Expectations and experiences of eHealth in primary care: A qualitative practicebased investigation [ J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2009,78(9): 588-604.
[31]Wu C H,Chen S C.Understanding the relationships of critical factors to Facebook educational usage intention [J].Internet Research,2015,25(2): 262-278.
[32]Gregor S.The nature of theory in information systems [J].MIS Quarterly,2006: 611-642.
[33]Burton-Jones A,Straub Jr D W.Reconceptualizing system usage:An approach and empirical test [ J].Information Systems Research,2006,17(3): 228-246.
[34]Venkatesh V,Brown S A,Maruping L M,et al.Predicting different conceptualizations of system use: The competing roles of behavioral intention,facilitating conditions,and behavioral expectation [J].MIS Quarterly,2008: 483-502.
[35]Petter S,DeLone W,McLean E.Measuring information systems success: Models,dimensions,measures,and interrelationships[J].European Journal of Information Systems,2008,17(3):236-263.
[36]Benbasat I,Barki H.Quo vadis TAM? [J].Journal of the Association for Information Systems,2007,8(4): 211-218.
[37]Archer N,Fevrier-Thomas U,Lokker C,et al.Personal health records: A scoping review [J].Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,2011,18(4): 515-522.
[38]Holden R J,Karsh B T.The technology acceptance model: Its past and its future in health care [J].Journal of Biomedical Informatics,2010,43(1): 159-172.
[39]Klein R,Rai A.Interfirm strategic information flows in logistics supply chain relationships [J].MIS Quarterly,2009: 735-762.
[40]Chiu C M,Wang E T G.Understanding Web-based learning continuance intention: The role of subjective task value [J].Information & Management,2008,45(3): 194-201.
[41]Chiu C M,Hsu M H,Wang E T G.Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories [J].Decision Support Systems,2006,42(3): 1872-1888.
[42]Zani W.Blueprint for MIS [J].Harvard Business Review,1970,48(6): 95-100.
[43]Rockart JF.Chief executives define their own data needs [J].Harvard Business Review,1979,57(2): 81-93.
[44]Zmud,Rober W.Individual differences and MIS success: A review of the empirical literature [J].Management science,1979(25): 966-979.
[45]Ives B,Olson M H.User involvement and MIS success: A review of research [J].Management Science,1984,30(5): 586-603.
[46]Keen P.MIS research: Reference disciplines and a cumulative tradition [ C].Proceedings of International Conference on Information Systems,Philadelphia,PA.1980: 9-18.
[47]Delone W H,Mclean E R.Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable [ J].Information Systems Research,1992,3(1): 60-95.
[48]Swanson E Burton.Management information system appreciation and involvement [J].Management Science,1974(21): 178-188.
[49]Bailey J E,Pearson S W.Development of a tool for measuring and analyzing computer user satisfaction [ J].Management Science,1983,29(5): 530-545.
[50]Chismar W G,Kriebel C H.A method for assessing the economic impact of information systems technology on organizations [C].Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Information Systems.Indianapolis Indiana,1985: 45-56.
[51]DeLone W H,McLean E R.The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update [J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2003,19(4): 9-30.
[52]Sedon P,Kiew M.A partial test and development of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [C].Proceeding of the Fifteenth International Conference on Information Systems,1995:99-110.
[53]Rai A,Lang S S,Welker R B.Assessing the validity of IS success models: An empirical test and theoretical analysis [J].Information Systems Research,2002,13(1): 50-69.
[54]Guimaraes T,Igbaria M.Client/server system success: Exploring the human side [J].Decision Sciences,1997,28(4): 851-876.
[55]Igbaria M,Tan M.The consequences of information technology acceptance on subsequent individual performance [ J ].Information & Management,1997,32(3): 113-121.
[56]Torkzadeh G,Doll W J.The development of a tool for measuring the perceived impact of information technology on work [J].Omega-international Journal of Management Science,1999,27(3): 327-339.
[57]Weill P,Vitale M.Assessing the health of an information systems applications portfolio: An example from process manufacturing[J].MIS Quarterly,1999: 601-624.
[58]Goodhue D L,Thompson R L.Task-technology fit and individual performance [J].MIS Quarterly,1995: 213-236.
[59]Etezadi-Amoli J,Farhoomand A F.A structural model of end user computing satisfaction and user performance [J].Information &Management,1996,30(2): 65-73.
[60]Teo T S H,Wong P K.An empirical study of the performance impact of computerization in the retail industry [J].Omega,1998,26(5): 611-621.
[61]Wixom B H,Watson H J.An empirical investigation of the factors affecting data warehousing success [J].MIS Quarterly,2001:17-41.
[62]Seddon P B.A respecification and extension of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Research,1997,8(3): 240-253.
[63]Young D,Benamati J.Differences in public Web sites: The current state of large US firms [J].Journal of Electronic Commerce Research,2000,1(3): 94-105.
[64]Delone W H,Mclean E R.Measuring e-commerce success:Applying the DeLone & McLean information systems success model [J].International Journal of Electronic Commerce,2004,9(1): 31-47.
[65]Jennex M,Olfman L,Panthawi P,et al.An organizational memory information systems success model: An extension of DeLone and McLean's I/S success model [C].Proceedings of the Thirty-First Hawaii International Conference on.IEEE,1998(1): 157-165.
[66]Yoon H S,Occeña L G.Influencing factors of trust in consumerto-consumer electronic commerce with gender and age [J].International Journal of Information Management,2015,35(3):352-363.
[67]Ghobakhloo M,Hong T S,Standing C.Business-to-businesselectronic commerce success: A supply network perspective [J].Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce,2014,24(4): 312-341.
[68]Beck R,Pahlke I,Seebach C.Knowledge exchange and symbolic action in social media-enabled electronic networks of practice: A multilevel perspective on knowledge seekers and contributors[J].Management Information Systems Quarterly,2014,38(4):1245-1270.
[69]Tsai W H,Chen H C,Chang J C,et al.Performance of the internal audit department under ERP systems: Empirical evidence from Taiwanese firms [J].Enterprise Information Systems,2015,9(7): 725-742.
[70]Poelmans S,Wessa P.A constructivist approach in a blended elearning environment for statistics [J].Interactive Learning Environments,2015,23(3): 385-401.
[71]Goo J,Huang C D,Koo C.Learning for healthy outcomes:Exploration and exploitation with electronic medical records [J].Information & Management,2015,52(5): 550-562.
[72]Tsai W H,Chou Y W,Leu J D,et al.Investigation of the mediating effects of IT governance-value delivery on service quality and ERP performance [ J].Enterprise Information Systems,2015,9(2): 139-160.
[73]Al-Jabri I M.Antecedents of user satisfaction with ERP systems:Mediation analyses [J].Kybernetes,2015,44(1): 107-123.
[74]Seddon P B.A respecification and extension of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Research,1997,8(3): 240-253.
[75]Rouibah K,Lowry P B,Almutairi L.Dimensions of business-toconsumer (B2C) systems success in Kuwait: Testing a modified DeLone and McLean IS success model in an e-commerce context[J].Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM),2015,23(3): 41-71.
[76]Sun J,Yang Z,Wang Y,et al.Rethinking e-commerce service quality does Website quality still suffice? [J].The Journal of Computer Information Systems,2015,55(4): 62-72.
[77]Chen Y,Yan X,Fan W.Examining the effects of decomposed perceived risk on consumer's online shopping behavior: A field study in China [J].Engineering Economics,2015,26(3):315-326.
[78]Matayong S,Kamil Mahmood A.The review of approaches to knowledge management system studies [J].Journal of Knowledge Management,2013,17(3): 472-490.
[79]Luo S H,Lee G G.Key factors for knowledge management implementation [ J].Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal,2013,41(3): 463-475.
[80]Esmaeilzadeh P,Sambasivan M,Kumar N,et al.Adoption of clinical decision support systems in a developing country:Antecedents and outcomes of physician's threat to perceived professional autonomy [J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2015,84(8) 8: 548-560.
[81]Ancker J S,Kern L M,Edwards A,et al.How is the electronic health record being used? Use of EHR data to assess physicianlevel variability in technology use [J].Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,2014,21(6): 1001-1008.
[82]Nguyen L,Bellucci E,Nguyen L T.Electronic health records implementation: An evaluation of information system impact and contingency factors [ J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2014,83(11): 779-796.
[83]Lin H F.Measuring online learning systems success: Applying the updated DeLone and McLean model [J].Cyberpsychology &Behavior the Impact of the Internet Multimedia & Virtual Reality on Behavior & Society,2007,10(6): 817-820.
[84]Lin H F.Interorganizational and organizational determinants ofplanning effectiveness for Internet-based interorganizational systems [J].Information & Management,2006,43(4): 423-433.
[85]Lee G G,Lin H F,Pai J C.Influence of environmental and organizational factors on the success of internet-based interorganizational systems planning [J].Internet Research,2005,15(5): 527-543.
[86]Dwivedi Y K,Kapoor K K,Williams M D,et al.RFID systems in libraries: An empirical examination of factors affecting system use and user satisfaction [J].International Journal of Information Management,2013,33(2): 367-377.
[ 87]Wang Y S.Assessing e-commerce systems success: A respecification and validation of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Journal,2008,18(5):529-557.
[88]Rana N P,Dwivedi Y K,Williams M D,et al.Investigating success of an e-government initiative: Validation of an integrated IS success model [J].Information Systems Frontiers,2015,17(1): 127-142.
[89]Hsiufen Lin.The role of online and offline features in sustaining virtual communities: An empirical study [J].Internet Research,2007,17(2): 119-138.
[90]Lee G G.Determinants of success for online communities: An empirical study [J].Behaviour & Information Technology,2006,25(6): 479-488.
[91]Lin H F.Determining the relative importance of mobile banking quality factors [J].Computer Standards & Interfaces,2013,35(2): 195-204.
[92]Lin H F.Antecedents of the stage-based knowledge management evolution [J].Journal of Knowledge Management,2011,15(1): 136-155.
[93]Shareef M A,Kumar V,Kumar U,et al.E-government adoption model ( GAM ): Differing service maturity levels [ J ].Government Information Quarterly,2011,28(1): 17-35.
[94]Wang Y S,Li H T,Li C R,et al.A model for assessing blogbased learning systems success [J].Online Information Review,2014,38(7): 969-990.
[95]Garrison G,Wakefield R L,Kim S.The effects of IT capabilities and delivery model on cloud computing success and firm performance for cloud supported processes and operations [J].International Journal of Information Management,2015,35(4):377-393.
[96]Venkatesh V,Sykes T A.Digital divide initiative success in developing countries: A longitudinal field study in a village in India [J].Information Systems Research,2013,24(2): 239-260.(https://www.daowen.com)
[97]Ecer F.A hybrid banking websites quality evaluation model using AHP and COPRAS-G: A Turkey case [J].Technological and Economic Development of Economy,2014,20(4): 758-782.
[98]Hsieh P J.Healthcare professionals’ use of health clouds:Integrating technology acceptance and status quo bias perspectives[J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2015,84(7): 512-523.
[99]Bui M T,Jeng D J F,Lin C.The importance of attribution connecting online travel communities with online travel agents[J].Cornell Hospitality Quarterly,2014(56): 285-297.
[100]Liaw S S,Huang H M.Perceived satisfaction,perceived usefulness and interactive learning environments as predictors to self-regulation in e-learning environments [J].Computers &Education,2013,60(1): 14-24.
[101]Soror A A,Hammer B I,Steelman Z R,et al.Good habits gone bad: Explaining negative consequences associated with the useof mobile phones from a dual-systems perspective [ J].Information Systems Journal,2015(4): 403-427.
[102]Kim C,Lee I S,Wang T,et al.Evaluating effects of mobile CRM on employees’ performance [J].Industrial Management& Data Systems,2015,115(4): 740-764.
[103]Koo C,Chung N,Kim H W.Examining explorative and exploitative uses of smartphones: a user competence perspective[J].Information Technology & People,2015,28(1): 133-162.
[104]Ryu M H,Kim J,Kim S.Factors affecting application developers’ loyalty to mobile platforms [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2014(40): 78-85.
[105]Jung H J.Ubiquitous learning:Determinants impacting learners’satisfaction and performance with smartphones [J].Language Learning and Technology,2014,18(3): 97-119.
[106]Okazaki S,Castañeda J A,Sanz S,et al.Physicians' appraisal of mobile health monitoring [J].The Service Industries Journal,2013,33(13-14): 1326-1344.
[107]Pu Y H,Chiu P S,Chen T S,et al.The design and implementation of a Mobile Library APP system [J].Library Hi Tech,2015,33(1): 15-31.
【作者简介】
通过表7可见,D&M 信息系统成功模型研究的热点,主要集中在在线学习[70][71]、企业资源计划[72][73][74]、电子商务[75][76][77]、社交网络和社交媒体[102][103][104]、知识管理[78][79]和医疗健康[80][81][82[]等研究范围。这些研究对象在一定程度上反映了近年来信息系统成功模型的应用已经涉及教育、经济、政治、医疗和互联网等各个领域,进一步展现了模型具有良好的应用性。信息系统成功模型在施引文献中的实际应用主要是通过两种方式:一种主要是利用D&M 信息系统成功模型中的相关变量或概念为指导对现实中具体问题进行的研究;另一种则是D&M 信息系统成功模型与其他模型相结合或者加入其他变量探讨实际问题。下面通过实例来展示这两种形式在研究热点中的应用。
第一种应用:Lin 大多研究都是针对网络环境下的信息系统成功的分析,如通过对232名学生进行调查分析,研究结果发现,系统质量、信息质量和服务质量对于学生在线学习系统的成功都具有显著影响[83];对网络环境下通过组织间和组织内两方面来探究组织间信息系统成功的影响变量[84]。Lee 等通过实证研究台湾202位信息系统管理者对研究模型中构面进行测试,并利用结构方程技术对研究模型进行评估,研究发现,环境因素中的“交易伙伴影响”变量及组织因素中的变量对组织间系统计划成功都具有显著性影响[85]。Dwivedi 等则将信息系统成功模型应用到图书馆领域中,探讨了射频技术(radio frequency identification,RFID)在图书馆中的应用,分析了RFID 系统的信息质量、系统质量和服务质量对用户使用及用户满意的影响,研究得出,射频技术在图书馆管理与服务中是十分受欢迎的技术之一[86]。Nguyen L,Bellucci E,Nguyen L T基于信息系统成功模型,评估电子病历中信息系统的作用和偶然性因素的影响[93]。此外,还有学者将信息系统成功模型应用到其他领域的研究,如对网络环境下的电子商务[87]、电子政务[88]、虚拟社区[89][90]、移动银行[91]、知识管理[92]等领域进行了探究。
第二种应用:Wu C H,Chen S C 通过构建包含信息质量、系统质量、功能质量和社会影响的概念框架,去探索影响Facebook用户教育性使用意愿的关键因素[102]。Shareef 等利用结构方程模型的方法,将TAM 与D&M 模型的结合对台湾地区的B2C(businessto-consumer)电子商务系统用户持续使用意愿进行了研究,研究发现D&M 信息系统成功模型中的信息质量、系统质量和服务质量对用户感知有用和用户满意都具有正向的影响[93]。Wang 等则通过将D&M 信息系统成功模型与教育技术成功模型相结合,对在线博客学习系统的影响因素进行了研究,由于在线博客学习对于网络环境的特殊要求,该研究将信息质量这一变量分为内容质量和链接质量两个维度,并分别分析了它们与用户满意及系统使用的关系[94]。
另外对云计算[95]、数字鸿沟[96]、网页质量[95][97]等问题的探讨,则表明信息系统成功研究越来越具体到现实的问题中。当然,其中也出现了很多学科间交叉的研究,如Hsieh 通过将云存储云计算与医疗行业相结合,研究专业医疗团队在使用云技术的接受情况和存在偏见等[98]。My-Trinh 等则基于归因理论对在线旅游社区的用户使用意愿进行了研究,研究得出高质量的信息服务可以为用户提供良好的信息反馈,有助于提高在线旅游社区的用户粘性[99]。Liaw 和Huang 从交互环境视角下对在线学习系统的应用进行研究,对196名大学生在使用在线学习系统数月后进行问卷调查,通过实证研究发现,感知有用和感知满意等在线学习系统成功影响因素都受到交互学习环境的影响[100]。
4.3 研究趋势展望
通过对近三年(2013—2026年)施引文献的关键词词频统计和相关文献内容阅读分析后发现,D&M 信息系统成功模型研究趋势主要表现在两个方面:
趋势之一主要体现在研究方向上,在互联网领域如虚拟社区、在线学习;医疗领域如医疗健康系统、电子病历;经济领域如电子商务;政治领域如电子政务等。这些研究中有的是直接利用D&M信息系统成功模型作为理论基础对具体问题进行的分析,更多一些则是通过将D&M 信息系统成功模型与相关理论结合对实际问题的探究。无论如何,信息系统成功模型的研究在多个领域和许多实际问题中的应用趋势不可阻挡。
趋势之二体现在研究平台上,通过对2013—2026年的施引文献内容进行分析不难发现,其中以移动平台为研究对象的信息系统成功研究探讨逐渐增多[101][102][103],这与时下移动终端设备及移动终端应用的普及是相辅相成的。如Ryu 等对用户面向移动平台如Google 或Apple 提供的应用平台使用忠诚的影响因素进行的研究,通过研究发现满意是用户忠实使用某一移动平台的重要影响变量,而移动平台的软件开发水平则决定了用户的满意度,研究还发现可信度与忠诚度之间并没有直接的影响[104];Jung 则对用户在泛在学习环境中使用智能手机的满意度和绩效影响变量展开研究,这也说明了移动智能终端设备作为当下及未来用户用于学习的重要工具之一[105]。Okazaki 等学者则对移动环境下医疗监控问题进行了探究,研究发现自我效能和兼容性是用户使用移动医疗监控信息系统的重要影响变量[106]。Pu 则对移动图书馆APP 的设计和应用进行了研究[107]。
5 结 语
随着信息系统在人们生活、工作和娱乐活动中广泛的应用和渗透,信息系统成功研究已受到越来越多的学者关注。DeLone 和McLean 于2026年发表的论文“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”提出了更新的信息系统成功模型,对信息系统成功研究产生了巨大影响。本研究针对引用了该文且被SSCI 数据库收录的期刊论文,结合论文发表年代、发文作者、发文作者机构、发文国家/地区、发文领域和ESI 论文等进行了统计分析。同时,结合关键词词频统计总结出近三年来信息系统成功模型应用研究的热点。最后,通过对施引文献的内容分析,发现信息系统成功模型的应用领域和应用环境越来越广。展望未来,面对移动互联网和物联网等新环境,信息系统的成功还会不断地面临新的问题,有待国内外相关学者积极开展系统和深入的研究,推动各类信息系统在实际应用中获得成功。
参考文献
[1]Vodanovich S,Sundaram D,Myers M.Research commentarydigital natives and ubiquitous information systems [ J ].Information Systems Research,2010,21(4): 711-723.
[2]Shannon C E,Weaver W.The mathematical theory of communication [M].Urbana,IL: University of Illinois Press,1949.
[3]Mason R O.Measuring information output: A communication systems approach [J].Information & Management,1978,1(78): 219-234.
[4]DeLone W H,McLean E R.The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update [J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2003,19(4): 9-30.
[5]Hong S,Katerattanakul P,Hong S K,et al.Usage and perceived impact of data warehouses: A study in Korean financial companies[J].International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making,2006,5(2): 297-315.
[6]Lai J Y.Assessment of employees’ perceptions of service quality and satisfaction with e-business [J].International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,2006,64(9): 926-938.
[7]Wang Y S,Liao Y W.The conceptualization and measurement of m-commerce user satisfaction [ J ].Computers in Human Behavior,2007,23(1): 381-398.
[8]Lin H F.The impact of website quality dimensions on customer satisfaction in the B2C e-commerce context [J].Total Quality Management and Business Excellence,2007,18(4): 363-378.
[9]Gil-García J R,Pardo T A.E-government success factors:Mapping practical tools to theoretical foundations [J].Government Information Quarterly,2005,22(2): 187-216.
[10]Prybutok V R,Zhang X,Ryan S D.Evaluating leadership,IT quality,and net benefits in an e-government environment [J].Information & Management,2008,45(3): 143-152.
[11]Connell N A D,Young T P.Evaluating healthcare information systems through an “enterprise”perspective [J].Information &Management,2007,44(4): 433-440.
[12]Shahmoradi L,Ahmadi M,Haghani H.Determining the most important evaluation indicators of healthcare information systems(HCIS) in Iran [J].Health Information Management Journal,2007,36(1): 13-22.
[13]Ong C S,Lai J Y.Gender differences in perceptions and relationships among dominants of e-learning acceptance [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2006,22(5): 816-829.
[14]Wang Y S,Wang H Y,Shee D Y.Measuring e-learning systems success in an organizational context: Scale development and validation [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2007,23(4):1792-1808.
[15]Lin H F.Measuring online learning systems success: Applying the updated DeLone and McLean model [J].Cyberpsychology &Behavior,2007,10(6): 817-820.
[16]Barczak G,Sultan F,Hultink E J.Determinants of IT usage and new product performance[J].Journal of Product Innovation Management,2007,24(6): 600-613.
通过表7可见,D&M 信息系统成功模型研究的热点,主要集中在在线学习[70][71]、企业资源计划[72][73][74]、电子商务[75][76][77]、社交网络和社交媒体[102][103][104]、知识管理[78][79]和医疗健康[80][81][82[]等研究范围。这些研究对象在一定程度上反映了近年来信息系统成功模型的应用已经涉及教育、经济、政治、医疗和互联网等各个领域,进一步展现了模型具有良好的应用性。信息系统成功模型在施引文献中的实际应用主要是通过两种方式:一种主要是利用D&M 信息系统成功模型中的相关变量或概念为指导对现实中具体问题进行的研究;另一种则是D&M 信息系统成功模型与其他模型相结合或者加入其他变量探讨实际问题。下面通过实例来展示这两种形式在研究热点中的应用。
[17]Cui L,Zhang C,Zhang C,et al.Exploring IT adoption process in shanghai firms: An empirical study [J].Journal of Global Information Management,2008,16(2): 1-17.
[18]Avlonitis G J,Panagopoulos N G.Antecedents and consequences of CRM technology acceptance in the sales force [J].Industrial Marketing Management,2005,34(4): 355-368.
[19]Xue Y,Liang H,Boulton W R,et al.ERP implementation failures in China: Case studies with implications for ERP vendors[J].International Journal of Production Economics,2005,97(3): 279-295.
[20]Wu J H,Wang Y M.Measuring ERP success:The ultimate users'view [J].International Journal of Operations & Production Management,2006,26(8): 882-903.
[21]Wang E T G,Ying T C,Jiang J J,et al.Group cohesion in organizational innovation: An empirical examination of ERP implementation [ J].Information and Software Technology,2006,48(4): 235-244.
[22]Lin H Y,Hsu P Y,Ting P H.ERP systems success: An integration of IS success model and balanced scorecard [J].Journal of Research and Practice in Information Technology,2006,38(3): 215-228.
第一种应用:Lin 大多研究都是针对网络环境下的信息系统成功的分析,如通过对232名学生进行调查分析,研究结果发现,系统质量、信息质量和服务质量对于学生在线学习系统的成功都具有显著影响[83];对网络环境下通过组织间和组织内两方面来探究组织间信息系统成功的影响变量[84]。Lee 等通过实证研究台湾202位信息系统管理者对研究模型中构面进行测试,并利用结构方程技术对研究模型进行评估,研究发现,环境因素中的“交易伙伴影响”变量及组织因素中的变量对组织间系统计划成功都具有显著性影响[85]。Dwivedi 等则将信息系统成功模型应用到图书馆领域中,探讨了射频技术(radio frequency identification,RFID)在图书馆中的应用,分析了RFID 系统的信息质量、系统质量和服务质量对用户使用及用户满意的影响,研究得出,射频技术在图书馆管理与服务中是十分受欢迎的技术之一[86]。Nguyen L,Bellucci E,Nguyen L T基于信息系统成功模型,评估电子病历中信息系统的作用和偶然性因素的影响[93]。此外,还有学者将信息系统成功模型应用到其他领域的研究,如对网络环境下的电子商务[87]、电子政务[88]、虚拟社区[89][90]、移动银行[91]、知识管理[92]等领域进行了探究。
[23]Chiu C M,Hsu M H,Wang E T G.Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories [J].Decision Support Systems,2006,42(3): 1872-1888.
[24]Kulkarni U R,Ravindran S,Freeze R.A knowledge management success model: Theoretical development and empirical validation[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2006,23(3): 309-347.
第二种应用:Wu C H,Chen S C 通过构建包含信息质量、系统质量、功能质量和社会影响的概念框架,去探索影响Facebook用户教育性使用意愿的关键因素[102]。Shareef 等利用结构方程模型的方法,将TAM 与D&M 模型的结合对台湾地区的B2C(businessto-consumer)电子商务系统用户持续使用意愿进行了研究,研究发现D&M 信息系统成功模型中的信息质量、系统质量和服务质量对用户感知有用和用户满意都具有正向的影响[93]。Wang 等则通过将D&M 信息系统成功模型与教育技术成功模型相结合,对在线博客学习系统的影响因素进行了研究,由于在线博客学习对于网络环境的特殊要求,该研究将信息质量这一变量分为内容质量和链接质量两个维度,并分别分析了它们与用户满意及系统使用的关系[94]。
[25]Petter S,DeLone W,McLean E.Measuring information systems success: Models,dimensions,measures,and interrelationships[J].European Journal of Information Systems,2008,17(3):236-263.
[26]Kulkarni U R,Ravindran S,Freeze R.A knowledge management success model: Theoretical development and empirical validation[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2006,23(3): 309-347.
[27]Wu J H,Wang Y M.Measuring KMS success: A respecification of the DeLone and McLean's model [ J].Information &Management,2006,43(6): 728-739.
[28]Ha S H,Noh M J,Choi S B.Difference in the adoption of internet open markets between transition and established market economies [J].Electronic Commerce Research,2014,14(4):531-558.
另外对云计算[95]、数字鸿沟[96]、网页质量[95][97]等问题的探讨,则表明信息系统成功研究越来越具体到现实的问题中。当然,其中也出现了很多学科间交叉的研究,如Hsieh 通过将云存储云计算与医疗行业相结合,研究专业医疗团队在使用云技术的接受情况和存在偏见等[98]。My-Trinh 等则基于归因理论对在线旅游社区的用户使用意愿进行了研究,研究得出高质量的信息服务可以为用户提供良好的信息反馈,有助于提高在线旅游社区的用户粘性[99]。Liaw 和Huang 从交互环境视角下对在线学习系统的应用进行研究,对196名大学生在使用在线学习系统数月后进行问卷调查,通过实证研究发现,感知有用和感知满意等在线学习系统成功影响因素都受到交互学习环境的影响[100]。
4.3 研究趋势展望
通过对近三年(2013—2026年)施引文献的关键词词频统计和相关文献内容阅读分析后发现,D&M 信息系统成功模型研究趋势主要表现在两个方面:
[29]Song J,Kim J,Jones D R,et al.Application discoverability and user satisfaction in mobile application stores: An environmental psychology perspective [J].Decision Support Systems,2014(59): 37-51.
趋势之一主要体现在研究方向上,在互联网领域如虚拟社区、在线学习;医疗领域如医疗健康系统、电子病历;经济领域如电子商务;政治领域如电子政务等。这些研究中有的是直接利用D&M信息系统成功模型作为理论基础对具体问题进行的分析,更多一些则是通过将D&M 信息系统成功模型与相关理论结合对实际问题的探究。无论如何,信息系统成功模型的研究在多个领域和许多实际问题中的应用趋势不可阻挡。
[30]Flynn D,Gregory P,Makki H,et al.Expectations and experiences of eHealth in primary care: A qualitative practicebased investigation [ J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2009,78(9): 588-604.
[31]Wu C H,Chen S C.Understanding the relationships of critical factors to Facebook educational usage intention [J].Internet Research,2015,25(2): 262-278.
[32]Gregor S.The nature of theory in information systems [J].MIS Quarterly,2006: 611-642.
[33]Burton-Jones A,Straub Jr D W.Reconceptualizing system usage:An approach and empirical test [ J].Information Systems Research,2006,17(3): 228-246.
趋势之二体现在研究平台上,通过对2013—2026年的施引文献内容进行分析不难发现,其中以移动平台为研究对象的信息系统成功研究探讨逐渐增多[101][102][103],这与时下移动终端设备及移动终端应用的普及是相辅相成的。如Ryu 等对用户面向移动平台如Google 或Apple 提供的应用平台使用忠诚的影响因素进行的研究,通过研究发现满意是用户忠实使用某一移动平台的重要影响变量,而移动平台的软件开发水平则决定了用户的满意度,研究还发现可信度与忠诚度之间并没有直接的影响[104];Jung 则对用户在泛在学习环境中使用智能手机的满意度和绩效影响变量展开研究,这也说明了移动智能终端设备作为当下及未来用户用于学习的重要工具之一[105]。Okazaki 等学者则对移动环境下医疗监控问题进行了探究,研究发现自我效能和兼容性是用户使用移动医疗监控信息系统的重要影响变量[106]。Pu 则对移动图书馆APP 的设计和应用进行了研究[107]。
5 结 语
[34]Venkatesh V,Brown S A,Maruping L M,et al.Predicting different conceptualizations of system use: The competing roles of behavioral intention,facilitating conditions,and behavioral expectation [J].MIS Quarterly,2008: 483-502.
[35]Petter S,DeLone W,McLean E.Measuring information systems success: Models,dimensions,measures,and interrelationships[J].European Journal of Information Systems,2008,17(3):236-263.
随着信息系统在人们生活、工作和娱乐活动中广泛的应用和渗透,信息系统成功研究已受到越来越多的学者关注。DeLone 和McLean 于2026年发表的论文“The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success:A ten-year update”提出了更新的信息系统成功模型,对信息系统成功研究产生了巨大影响。本研究针对引用了该文且被SSCI 数据库收录的期刊论文,结合论文发表年代、发文作者、发文作者机构、发文国家/地区、发文领域和ESI 论文等进行了统计分析。同时,结合关键词词频统计总结出近三年来信息系统成功模型应用研究的热点。最后,通过对施引文献的内容分析,发现信息系统成功模型的应用领域和应用环境越来越广。展望未来,面对移动互联网和物联网等新环境,信息系统的成功还会不断地面临新的问题,有待国内外相关学者积极开展系统和深入的研究,推动各类信息系统在实际应用中获得成功。
参考文献
[36]Benbasat I,Barki H.Quo vadis TAM? [J].Journal of the Association for Information Systems,2007,8(4): 211-218.
[1]Vodanovich S,Sundaram D,Myers M.Research commentarydigital natives and ubiquitous information systems [ J ].Information Systems Research,2010,21(4): 711-723.
[37]Archer N,Fevrier-Thomas U,Lokker C,et al.Personal health records: A scoping review [J].Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,2011,18(4): 515-522.
[2]Shannon C E,Weaver W.The mathematical theory of communication [M].Urbana,IL: University of Illinois Press,1949.
[38]Holden R J,Karsh B T.The technology acceptance model: Its past and its future in health care [J].Journal of Biomedical Informatics,2010,43(1): 159-172.
[3]Mason R O.Measuring information output: A communication systems approach [J].Information & Management,1978,1(78): 219-234.
[39]Klein R,Rai A.Interfirm strategic information flows in logistics supply chain relationships [J].MIS Quarterly,2009: 735-762.
[4]DeLone W H,McLean E R.The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update [J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2003,19(4): 9-30.
[40]Chiu C M,Wang E T G.Understanding Web-based learning continuance intention: The role of subjective task value [J].Information & Management,2008,45(3): 194-201.
[5]Hong S,Katerattanakul P,Hong S K,et al.Usage and perceived impact of data warehouses: A study in Korean financial companies[J].International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making,2006,5(2): 297-315.
[41]Chiu C M,Hsu M H,Wang E T G.Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories [J].Decision Support Systems,2006,42(3): 1872-1888.
[6]Lai J Y.Assessment of employees’ perceptions of service quality and satisfaction with e-business [J].International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,2006,64(9): 926-938.
[42]Zani W.Blueprint for MIS [J].Harvard Business Review,1970,48(6): 95-100.
[7]Wang Y S,Liao Y W.The conceptualization and measurement of m-commerce user satisfaction [ J ].Computers in Human Behavior,2007,23(1): 381-398.
[43]Rockart JF.Chief executives define their own data needs [J].Harvard Business Review,1979,57(2): 81-93.
[8]Lin H F.The impact of website quality dimensions on customer satisfaction in the B2C e-commerce context [J].Total Quality Management and Business Excellence,2007,18(4): 363-378.
[44]Zmud,Rober W.Individual differences and MIS success: A review of the empirical literature [J].Management science,1979(25): 966-979.
[9]Gil-García J R,Pardo T A.E-government success factors:Mapping practical tools to theoretical foundations [J].Government Information Quarterly,2005,22(2): 187-216.
[45]Ives B,Olson M H.User involvement and MIS success: A review of research [J].Management Science,1984,30(5): 586-603.
[10]Prybutok V R,Zhang X,Ryan S D.Evaluating leadership,IT quality,and net benefits in an e-government environment [J].Information & Management,2008,45(3): 143-152.
[46]Keen P.MIS research: Reference disciplines and a cumulative tradition [ C].Proceedings of International Conference on Information Systems,Philadelphia,PA.1980: 9-18.
[11]Connell N A D,Young T P.Evaluating healthcare information systems through an “enterprise”perspective [J].Information &Management,2007,44(4): 433-440.
[47]Delone W H,Mclean E R.Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable [ J].Information Systems Research,1992,3(1): 60-95.
[48]Swanson E Burton.Management information system appreciation and involvement [J].Management Science,1974(21): 178-188.
[12]Shahmoradi L,Ahmadi M,Haghani H.Determining the most important evaluation indicators of healthcare information systems(HCIS) in Iran [J].Health Information Management Journal,2007,36(1): 13-22.
[49]Bailey J E,Pearson S W.Development of a tool for measuring and analyzing computer user satisfaction [ J].Management Science,1983,29(5): 530-545.
[13]Ong C S,Lai J Y.Gender differences in perceptions and relationships among dominants of e-learning acceptance [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2006,22(5): 816-829.
[50]Chismar W G,Kriebel C H.A method for assessing the economic impact of information systems technology on organizations [C].Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Information Systems.Indianapolis Indiana,1985: 45-56.
[14]Wang Y S,Wang H Y,Shee D Y.Measuring e-learning systems success in an organizational context: Scale development and validation [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2007,23(4):1792-1808.
[51]DeLone W H,McLean E R.The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update [J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2003,19(4): 9-30.
[15]Lin H F.Measuring online learning systems success: Applying the updated DeLone and McLean model [J].Cyberpsychology &Behavior,2007,10(6): 817-820.
[52]Sedon P,Kiew M.A partial test and development of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [C].Proceeding of the Fifteenth International Conference on Information Systems,1995:99-110.
[16]Barczak G,Sultan F,Hultink E J.Determinants of IT usage and new product performance[J].Journal of Product Innovation Management,2007,24(6): 600-613.
[53]Rai A,Lang S S,Welker R B.Assessing the validity of IS success models: An empirical test and theoretical analysis [J].Information Systems Research,2002,13(1): 50-69.
[17]Cui L,Zhang C,Zhang C,et al.Exploring IT adoption process in shanghai firms: An empirical study [J].Journal of Global Information Management,2008,16(2): 1-17.
[54]Guimaraes T,Igbaria M.Client/server system success: Exploring the human side [J].Decision Sciences,1997,28(4): 851-876.
[18]Avlonitis G J,Panagopoulos N G.Antecedents and consequences of CRM technology acceptance in the sales force [J].Industrial Marketing Management,2005,34(4): 355-368.
[55]Igbaria M,Tan M.The consequences of information technology acceptance on subsequent individual performance [ J ].Information & Management,1997,32(3): 113-121.
[19]Xue Y,Liang H,Boulton W R,et al.ERP implementation failures in China: Case studies with implications for ERP vendors[J].International Journal of Production Economics,2005,97(3): 279-295.
[20]Wu J H,Wang Y M.Measuring ERP success:The ultimate users'view [J].International Journal of Operations & Production Management,2006,26(8): 882-903.
他接着又写些关于经典作家著作的排列问题,完全分类号的问题,单行本和中国共产党的历次代表大会的文献资料不用书次号的问题。不知孟先生写出这些是在作补充说明,帮助用者对《人大法》加深理解呢?还是什么?假使能写出较详细的补充说明,使用者更好地运用《人大法》,那还是十分必要的。可惜,孟先生
[21]Wang E T G,Ying T C,Jiang J J,et al.Group cohesion in organizational innovation: An empirical examination of ERP implementation [ J].Information and Software Technology,2006,48(4): 235-244.
[58]Goodhue D L,Thompson R L.Task-technology fit and individual performance [J].MIS Quarterly,1995: 213-236.
[22]Lin H Y,Hsu P Y,Ting P H.ERP systems success: An integration of IS success model and balanced scorecard [J].Journal of Research and Practice in Information Technology,2006,38(3): 215-228.
[59]Etezadi-Amoli J,Farhoomand A F.A structural model of end user computing satisfaction and user performance [J].Information &Management,1996,30(2): 65-73.
[23]Chiu C M,Hsu M H,Wang E T G.Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories [J].Decision Support Systems,2006,42(3): 1872-1888.
[60]Teo T S H,Wong P K.An empirical study of the performance impact of computerization in the retail industry [J].Omega,1998,26(5): 611-621.
[24]Kulkarni U R,Ravindran S,Freeze R.A knowledge management success model: Theoretical development and empirical validation[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2006,23(3): 309-347.
[61]Wixom B H,Watson H J.An empirical investigation of the factors affecting data warehousing success [J].MIS Quarterly,2001:17-41.
[25]Petter S,DeLone W,McLean E.Measuring information systems success: Models,dimensions,measures,and interrelationships[J].European Journal of Information Systems,2008,17(3):236-263.
[62]Seddon P B.A respecification and extension of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Research,1997,8(3): 240-253.
[26]Kulkarni U R,Ravindran S,Freeze R.A knowledge management success model: Theoretical development and empirical validation[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2006,23(3): 309-347.
[63]Young D,Benamati J.Differences in public Web sites: The current state of large US firms [J].Journal of Electronic Commerce Research,2000,1(3): 94-105.
[27]Wu J H,Wang Y M.Measuring KMS success: A respecification of the DeLone and McLean's model [ J].Information &Management,2006,43(6): 728-739.
[64]Delone W H,Mclean E R.Measuring e-commerce success:Applying the DeLone & McLean information systems success model [J].International Journal of Electronic Commerce,2004,9(1): 31-47.
[28]Ha S H,Noh M J,Choi S B.Difference in the adoption of internet open markets between transition and established market economies [J].Electronic Commerce Research,2014,14(4):531-558.
[65]Jennex M,Olfman L,Panthawi P,et al.An organizational memory information systems success model: An extension of DeLone and McLean's I/S success model [C].Proceedings of the Thirty-First Hawaii International Conference on.IEEE,1998(1): 157-165.
[29]Song J,Kim J,Jones D R,et al.Application discoverability and user satisfaction in mobile application stores: An environmental psychology perspective [J].Decision Support Systems,2014(59): 37-51.
[66]Yoon H S,Occeña L G.Influencing factors of trust in consumerto-consumer electronic commerce with gender and age [J].International Journal of Information Management,2015,35(3):352-363.
[30]Flynn D,Gregory P,Makki H,et al.Expectations and experiences of eHealth in primary care: A qualitative practicebased investigation [ J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2009,78(9): 588-604.
[31]Wu C H,Chen S C.Understanding the relationships of critical factors to Facebook educational usage intention [J].Internet Research,2015,25(2): 262-278.
[67]Ghobakhloo M,Hong T S,Standing C.Business-to-businesselectronic commerce success: A supply network perspective [J].Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce,2014,24(4): 312-341.
[32]Gregor S.The nature of theory in information systems [J].MIS Quarterly,2006: 611-642.
[33]Burton-Jones A,Straub Jr D W.Reconceptualizing system usage:An approach and empirical test [ J].Information Systems Research,2006,17(3): 228-246.
[68]Beck R,Pahlke I,Seebach C.Knowledge exchange and symbolic action in social media-enabled electronic networks of practice: A multilevel perspective on knowledge seekers and contributors[J].Management Information Systems Quarterly,2014,38(4):1245-1270.
[34]Venkatesh V,Brown S A,Maruping L M,et al.Predicting different conceptualizations of system use: The competing roles of behavioral intention,facilitating conditions,and behavioral expectation [J].MIS Quarterly,2008: 483-502.
.81 福建省 Fukien
.83 廣東省 Kwangtung
.85 廣西省 Kwangsi
.86 雲南省 Yunnan
.87 貴州省 Kweichow
.9 中國藩部 The outer territories of China
.91 滿州 東三省 Manchu The three Eastern
[70]Poelmans S,Wessa P.A constructivist approach in a blended elearning environment for statistics [J].Interactive Learning Environments,2015,23(3): 385-401.
[35]Petter S,DeLone W,McLean E.Measuring information systems success: Models,dimensions,measures,and interrelationships[J].European Journal of Information Systems,2008,17(3):236-263.
[36]Benbasat I,Barki H.Quo vadis TAM? [J].Journal of the Association for Information Systems,2007,8(4): 211-218.
[71]Goo J,Huang C D,Koo C.Learning for healthy outcomes:Exploration and exploitation with electronic medical records [J].Information & Management,2015,52(5): 550-562.
[37]Archer N,Fevrier-Thomas U,Lokker C,et al.Personal health records: A scoping review [J].Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,2011,18(4): 515-522.
[72]Tsai W H,Chou Y W,Leu J D,et al.Investigation of the mediating effects of IT governance-value delivery on service quality and ERP performance [ J].Enterprise Information Systems,2015,9(2): 139-160.
[38]Holden R J,Karsh B T.The technology acceptance model: Its past and its future in health care [J].Journal of Biomedical Informatics,2010,43(1): 159-172.
[73]Al-Jabri I M.Antecedents of user satisfaction with ERP systems:Mediation analyses [J].Kybernetes,2015,44(1): 107-123.
[39]Klein R,Rai A.Interfirm strategic information flows in logistics supply chain relationships [J].MIS Quarterly,2009: 735-762.
[74]Seddon P B.A respecification and extension of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Research,1997,8(3): 240-253.
[40]Chiu C M,Wang E T G.Understanding Web-based learning continuance intention: The role of subjective task value [J].Information & Management,2008,45(3): 194-201.
[41]Chiu C M,Hsu M H,Wang E T G.Understanding knowledge sharing in virtual communities: An integration of social capital and social cognitive theories [J].Decision Support Systems,2006,42(3): 1872-1888.
[75]Rouibah K,Lowry P B,Almutairi L.Dimensions of business-toconsumer (B2C) systems success in Kuwait: Testing a modified DeLone and McLean IS success model in an e-commerce context[J].Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM),2015,23(3): 41-71.
[42]Zani W.Blueprint for MIS [J].Harvard Business Review,1970,48(6): 95-100.
[76]Sun J,Yang Z,Wang Y,et al.Rethinking e-commerce service quality does Website quality still suffice? [J].The Journal of Computer Information Systems,2015,55(4): 62-72.
[43]Rockart JF.Chief executives define their own data needs [J].Harvard Business Review,1979,57(2): 81-93.
[77]Chen Y,Yan X,Fan W.Examining the effects of decomposed perceived risk on consumer's online shopping behavior: A field study in China [J].Engineering Economics,2015,26(3):315-326.
[44]Zmud,Rober W.Individual differences and MIS success: A review of the empirical literature [J].Management science,1979(25): 966-979.
[45]Ives B,Olson M H.User involvement and MIS success: A review of research [J].Management Science,1984,30(5): 586-603.
[78]Matayong S,Kamil Mahmood A.The review of approaches to knowledge management system studies [J].Journal of Knowledge Management,2013,17(3): 472-490.
[79]Luo S H,Lee G G.Key factors for knowledge management implementation [ J].Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal,2013,41(3): 463-475.
.662 加拉馬尼亞
.663 亞達那 Adana
.664 西威斯 Sivas
.665 德比孫 Trebizond
.666 亞美尼亞:挨爾斯倫 Armen
[47]Delone W H,Mclean E R.Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable [ J].Information Systems Research,1992,3(1): 60-95.
[80]Esmaeilzadeh P,Sambasivan M,Kumar N,et al.Adoption of clinical decision support systems in a developing country:Antecedents and outcomes of physician's threat to perceived professional autonomy [J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2015,84(8) 8: 548-560.
[48]Swanson E Burton.Management information system appreciation and involvement [J].Management Science,1974(21): 178-188.
[49]Bailey J E,Pearson S W.Development of a tool for measuring and analyzing computer user satisfaction [ J].Management Science,1983,29(5): 530-545.
[81]Ancker J S,Kern L M,Edwards A,et al.How is the electronic health record being used? Use of EHR data to assess physicianlevel variability in technology use [J].Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,2014,21(6): 1001-1008.
[50]Chismar W G,Kriebel C H.A method for assessing the economic impact of information systems technology on organizations [C].Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Information Systems.Indianapolis Indiana,1985: 45-56.
[82]Nguyen L,Bellucci E,Nguyen L T.Electronic health records implementation: An evaluation of information system impact and contingency factors [ J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2014,83(11): 779-796.
[51]DeLone W H,McLean E R.The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update [J].Journal of Management Information Systems,2003,19(4): 9-30.
[83]Lin H F.Measuring online learning systems success: Applying the updated DeLone and McLean model [J].Cyberpsychology &Behavior the Impact of the Internet Multimedia & Virtual Reality on Behavior & Society,2007,10(6): 817-820.
[52]Sedon P,Kiew M.A partial test and development of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [C].Proceeding of the Fifteenth International Conference on Information Systems,1995:99-110.
[84]Lin H F.Interorganizational and organizational determinants ofplanning effectiveness for Internet-based interorganizational systems [J].Information & Management,2006,43(4): 423-433.
[53]Rai A,Lang S S,Welker R B.Assessing the validity of IS success models: An empirical test and theoretical analysis [J].Information Systems Research,2002,13(1): 50-69.
[85]Lee G G,Lin H F,Pai J C.Influence of environmental and organizational factors on the success of internet-based interorganizational systems planning [J].Internet Research,2005,15(5): 527-543.
[54]Guimaraes T,Igbaria M.Client/server system success: Exploring the human side [J].Decision Sciences,1997,28(4): 851-876.
[86]Dwivedi Y K,Kapoor K K,Williams M D,et al.RFID systems in libraries: An empirical examination of factors affecting system use and user satisfaction [J].International Journal of Information Management,2013,33(2): 367-377.
[55]Igbaria M,Tan M.The consequences of information technology acceptance on subsequent individual performance [ J ].Information & Management,1997,32(3): 113-121.
[56]Torkzadeh G,Doll W J.The development of a tool for measuring the perceived impact of information technology on work [J].Omega-international Journal of Management Science,1999,27(3): 327-339.
.487 疴維爾内:不伊德多美,干達爾 Auvergne:Puy de Dome,Cantal
.488 馬爾也:克留斯 Marche:Creuse
.489 黎木性:高維也納,哥勒塞 Limousin:Haute Vienne,Correze
.49 西南 東南部 West,So
[57]Weill P,Vitale M.Assessing the health of an information systems applications portfolio: An example from process manufacturing[J].MIS Quarterly,1999: 601-624.
[88]Rana N P,Dwivedi Y K,Williams M D,et al.Investigating success of an e-government initiative: Validation of an integrated IS success model [J].Information Systems Frontiers,2015,17(1): 127-142.
[58]Goodhue D L,Thompson R L.Task-technology fit and individual performance [J].MIS Quarterly,1995: 213-236.
[89]Hsiufen Lin.The role of online and offline features in sustaining virtual communities: An empirical study [J].Internet Research,2007,17(2): 119-138.
[59]Etezadi-Amoli J,Farhoomand A F.A structural model of end user computing satisfaction and user performance [J].Information &Management,1996,30(2): 65-73.
[90]Lee G G.Determinants of success for online communities: An empirical study [J].Behaviour & Information Technology,2006,25(6): 479-488.
[60]Teo T S H,Wong P K.An empirical study of the performance impact of computerization in the retail industry [J].Omega,1998,26(5): 611-621.
[91]Lin H F.Determining the relative importance of mobile banking quality factors [J].Computer Standards & Interfaces,2013,35(2): 195-204.
[61]Wixom B H,Watson H J.An empirical investigation of the factors affecting data warehousing success [J].MIS Quarterly,2001:17-41.
[62]Seddon P B.A respecification and extension of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Research,1997,8(3): 240-253.
[92]Lin H F.Antecedents of the stage-based knowledge management evolution [J].Journal of Knowledge Management,2011,15(1): 136-155.
[63]Young D,Benamati J.Differences in public Web sites: The current state of large US firms [J].Journal of Electronic Commerce Research,2000,1(3): 94-105.
[93]Shareef M A,Kumar V,Kumar U,et al.E-government adoption model ( GAM ): Differing service maturity levels [ J ].Government Information Quarterly,2011,28(1): 17-35.
[94]Wang Y S,Li H T,Li C R,et al.A model for assessing blogbased learning systems success [J].Online Information Review,2014,38(7): 969-990.
[64]Delone W H,Mclean E R.Measuring e-commerce success:Applying the DeLone & McLean information systems success model [J].International Journal of Electronic Commerce,2004,9(1): 31-47.
[65]Jennex M,Olfman L,Panthawi P,et al.An organizational memory information systems success model: An extension of DeLone and McLean's I/S success model [C].Proceedings of the Thirty-First Hawaii International Conference on.IEEE,1998(1): 157-165.
[95]Garrison G,Wakefield R L,Kim S.The effects of IT capabilities and delivery model on cloud computing success and firm performance for cloud supported processes and operations [J].International Journal of Information Management,2015,35(4):377-393.
[66]Yoon H S,Occeña L G.Influencing factors of trust in consumerto-consumer electronic commerce with gender and age [J].International Journal of Information Management,2015,35(3):352-363.
[96]Venkatesh V,Sykes T A.Digital divide initiative success in developing countries: A longitudinal field study in a village in India [J].Information Systems Research,2013,24(2): 239-260.
[67]Ghobakhloo M,Hong T S,Standing C.Business-to-businesselectronic commerce success: A supply network perspective [J].Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce,2014,24(4): 312-341.
[97]Ecer F.A hybrid banking websites quality evaluation model using AHP and COPRAS-G: A Turkey case [J].Technological and Economic Development of Economy,2014,20(4): 758-782.
[98]Hsieh P J.Healthcare professionals’ use of health clouds:Integrating technology acceptance and status quo bias perspectives[J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2015,84(7): 512-523.
[68]Beck R,Pahlke I,Seebach C.Knowledge exchange and symbolic action in social media-enabled electronic networks of practice: A multilevel perspective on knowledge seekers and contributors[J].Management Information Systems Quarterly,2014,38(4):1245-1270.
[99]Bui M T,Jeng D J F,Lin C.The importance of attribution connecting online travel communities with online travel agents[J].Cornell Hospitality Quarterly,2014(56): 285-297.
[69]Tsai W H,Chen H C,Chang J C,et al.Performance of the internal audit department under ERP systems: Empirical evidence from Taiwanese firms [J].Enterprise Information Systems,2015,9(7): 725-742.
[70]Poelmans S,Wessa P.A constructivist approach in a blended elearning environment for statistics [J].Interactive Learning Environments,2015,23(3): 385-401.
[100]Liaw S S,Huang H M.Perceived satisfaction,perceived usefulness and interactive learning environments as predictors to self-regulation in e-learning environments [J].Computers &Education,2013,60(1): 14-24.
[71]Goo J,Huang C D,Koo C.Learning for healthy outcomes:Exploration and exploitation with electronic medical records [J].Information & Management,2015,52(5): 550-562.
[101]Soror A A,Hammer B I,Steelman Z R,et al.Good habits gone bad: Explaining negative consequences associated with the useof mobile phones from a dual-systems perspective [ J].Information Systems Journal,2015(4): 403-427.
[72]Tsai W H,Chou Y W,Leu J D,et al.Investigation of the mediating effects of IT governance-value delivery on service quality and ERP performance [ J].Enterprise Information Systems,2015,9(2): 139-160.
[102]Kim C,Lee I S,Wang T,et al.Evaluating effects of mobile CRM on employees’ performance [J].Industrial Management& Data Systems,2015,115(4): 740-764.
[73]Al-Jabri I M.Antecedents of user satisfaction with ERP systems:Mediation analyses [J].Kybernetes,2015,44(1): 107-123.
[103]Koo C,Chung N,Kim H W.Examining explorative and exploitative uses of smartphones: a user competence perspective[J].Information Technology & People,2015,28(1): 133-162.
[74]Seddon P B.A respecification and extension of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Research,1997,8(3): 240-253.
[104]Ryu M H,Kim J,Kim S.Factors affecting application developers’ loyalty to mobile platforms [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2014(40): 78-85.
[75]Rouibah K,Lowry P B,Almutairi L.Dimensions of business-toconsumer (B2C) systems success in Kuwait: Testing a modified DeLone and McLean IS success model in an e-commerce context[J].Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM),2015,23(3): 41-71.
[105]Jung H J.Ubiquitous learning:Determinants impacting learners’satisfaction and performance with smartphones [J].Language Learning and Technology,2014,18(3): 97-119.
[76]Sun J,Yang Z,Wang Y,et al.Rethinking e-commerce service quality does Website quality still suffice? [J].The Journal of Computer Information Systems,2015,55(4): 62-72.
[106]Okazaki S,Castañeda J A,Sanz S,et al.Physicians' appraisal of mobile health monitoring [J].The Service Industries Journal,2013,33(13-14): 1326-1344.
[77]Chen Y,Yan X,Fan W.Examining the effects of decomposed perceived risk on consumer's online shopping behavior: A field study in China [J].Engineering Economics,2015,26(3):315-326.
[107]Pu Y H,Chiu P S,Chen T S,et al.The design and implementation of a Mobile Library APP system [J].Library Hi Tech,2015,33(1): 15-31.
【作者简介】
[78]Matayong S,Kamil Mahmood A.The review of approaches to knowledge management system studies [J].Journal of Knowledge Management,2013,17(3): 472-490.
[79]Luo S H,Lee G G.Key factors for knowledge management implementation [ J].Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal,2013,41(3): 463-475.
[80]Esmaeilzadeh P,Sambasivan M,Kumar N,et al.Adoption of clinical decision support systems in a developing country:Antecedents and outcomes of physician's threat to perceived professional autonomy [J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2015,84(8) 8: 548-560.
[81]Ancker J S,Kern L M,Edwards A,et al.How is the electronic health record being used? Use of EHR data to assess physicianlevel variability in technology use [J].Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association,2014,21(6): 1001-1008.
[82]Nguyen L,Bellucci E,Nguyen L T.Electronic health records implementation: An evaluation of information system impact and contingency factors [ J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2014,83(11): 779-796.
[83]Lin H F.Measuring online learning systems success: Applying the updated DeLone and McLean model [J].Cyberpsychology &Behavior the Impact of the Internet Multimedia & Virtual Reality on Behavior & Society,2007,10(6): 817-820.
[84]Lin H F.Interorganizational and organizational determinants ofplanning effectiveness for Internet-based interorganizational systems [J].Information & Management,2006,43(4): 423-433.
[85]Lee G G,Lin H F,Pai J C.Influence of environmental and organizational factors on the success of internet-based interorganizational systems planning [J].Internet Research,2005,15(5): 527-543.
[86]Dwivedi Y K,Kapoor K K,Williams M D,et al.RFID systems in libraries: An empirical examination of factors affecting system use and user satisfaction [J].International Journal of Information Management,2013,33(2): 367-377.
[ 87]Wang Y S.Assessing e-commerce systems success: A respecification and validation of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success [J].Information Systems Journal,2008,18(5):529-557.
[88]Rana N P,Dwivedi Y K,Williams M D,et al.Investigating success of an e-government initiative: Validation of an integrated IS success model [J].Information Systems Frontiers,2015,17(1): 127-142.
[89]Hsiufen Lin.The role of online and offline features in sustaining virtual communities: An empirical study [J].Internet Research,2007,17(2): 119-138.
[90]Lee G G.Determinants of success for online communities: An empirical study [J].Behaviour & Information Technology,2006,25(6): 479-488.
[91]Lin H F.Determining the relative importance of mobile banking quality factors [J].Computer Standards & Interfaces,2013,35(2): 195-204.
[92]Lin H F.Antecedents of the stage-based knowledge management evolution [J].Journal of Knowledge Management,2011,15(1): 136-155.
[93]Shareef M A,Kumar V,Kumar U,et al.E-government adoption model ( GAM ): Differing service maturity levels [ J ].Government Information Quarterly,2011,28(1): 17-35.
[94]Wang Y S,Li H T,Li C R,et al.A model for assessing blogbased learning systems success [J].Online Information Review,2014,38(7): 969-990.
[95]Garrison G,Wakefield R L,Kim S.The effects of IT capabilities and delivery model on cloud computing success and firm performance for cloud supported processes and operations [J].International Journal of Information Management,2015,35(4):377-393.
[96]Venkatesh V,Sykes T A.Digital divide initiative success in developing countries: A longitudinal field study in a village in India [J].Information Systems Research,2013,24(2): 239-260.
[97]Ecer F.A hybrid banking websites quality evaluation model using AHP and COPRAS-G: A Turkey case [J].Technological and Economic Development of Economy,2014,20(4): 758-782.
[98]Hsieh P J.Healthcare professionals’ use of health clouds:Integrating technology acceptance and status quo bias perspectives[J].International Journal of Medical Informatics,2015,84(7): 512-523.
[99]Bui M T,Jeng D J F,Lin C.The importance of attribution connecting online travel communities with online travel agents[J].Cornell Hospitality Quarterly,2014(56): 285-297.
[100]Liaw S S,Huang H M.Perceived satisfaction,perceived usefulness and interactive learning environments as predictors to self-regulation in e-learning environments [J].Computers &Education,2013,60(1): 14-24.
[101]Soror A A,Hammer B I,Steelman Z R,et al.Good habits gone bad: Explaining negative consequences associated with the useof mobile phones from a dual-systems perspective [ J].Information Systems Journal,2015(4): 403-427.
[102]Kim C,Lee I S,Wang T,et al.Evaluating effects of mobile CRM on employees’ performance [J].Industrial Management& Data Systems,2015,115(4): 740-764.
[103]Koo C,Chung N,Kim H W.Examining explorative and exploitative uses of smartphones: a user competence perspective[J].Information Technology & People,2015,28(1): 133-162.
[104]Ryu M H,Kim J,Kim S.Factors affecting application developers’ loyalty to mobile platforms [J].Computers in Human Behavior,2014(40): 78-85.
[105]Jung H J.Ubiquitous learning:Determinants impacting learners’satisfaction and performance with smartphones [J].Language Learning and Technology,2014,18(3): 97-119.
[106]Okazaki S,Castañeda J A,Sanz S,et al.Physicians' appraisal of mobile health monitoring [J].The Service Industries Journal,2013,33(13-14): 1326-1344.
[107]Pu Y H,Chiu P S,Chen T S,et al.The design and implementation of a Mobile Library APP system [J].Library Hi Tech,2015,33(1): 15-31.
【作者简介】
王文韬,男,2026年生,武汉大学信息管理学院情报学专业博士研究生,研究方向为信息资源管理、信息分析、信息行为、信息系统。在国内外重要期刊发表学术论文20余篇,其中2篇论文发表在SSCI/SCI 收录的国际期刊上。
王文韬,男,2026年生,武汉大学信息管理学院情报学专业博士研究生,研究方向为信息资源管理、信息分析、信息行为、信息系统。在国内外重要期刊发表学术论文20余篇,其中2篇论文发表在SSCI/SCI 收录的国际期刊上。
王文韬,男,2026年生,武汉大学信息管理学院情报学专业博士研究生,研究方向为信息资源管理、信息分析、信息行为、信息系统。在国内外重要期刊发表学术论文20余篇,其中2篇论文发表在SSCI/SCI 收录的国际期刊上。
查先进,男,2026年生,博士,珞珈特聘教授,博士生导师,教育部“新世纪优秀人才支持计划”获得者。兼任中国信息经济学会常务理事、中国科学技术情报学会理事、中国科学技术情报学会情报理论方法与教育培训专业委员会副主任委员、国际信息科学和技术协会(ASIS&T)会员、国际信息系统协会(AIS)会员、湖北省信息学会理事等职。研究方向为信息分析、竞争情报、信息资源管理、信息行为、信息系统。在国内外重要期刊发表学术论文90余篇,其中近20篇论文发表在SSCI/SCI 收录的国际期刊上。
查先进,男,2026年生,博士,珞珈特聘教授,博士生导师,教育部“新世纪优秀人才支持计划”获得者。兼任中国信息经济学会常务理事、中国科学技术情报学会理事、中国科学技术情报学会情报理论方法与教育培训专业委员会副主任委员、国际信息科学和技术协会(ASIS&T)会员、国际信息系统协会(AIS)会员、湖北省信息学会理事等职。研究方向为信息分析、竞争情报、信息资源管理、信息行为、信息系统。在国内外重要期刊发表学术论文90余篇,其中近20篇论文发表在SSCI/SCI 收录的国际期刊上。
查先进,男,2026年生,博士,珞珈特聘教授,博士生导师,教育部“新世纪优秀人才支持计划”获得者。兼任中国信息经济学会常务理事、中国科学技术情报学会理事、中国科学技术情报学会情报理论方法与教育培训专业委员会副主任委员、国际信息科学和技术协会(ASIS&T)会员、国际信息系统协会(AIS)会员、湖北省信息学会理事等职。研究方向为信息分析、竞争情报、信息资源管理、信息行为、信息系统。在国内外重要期刊发表学术论文90余篇,其中近20篇论文发表在SSCI/SCI 收录的国际期刊上。
郭佳,女,2026年生,武汉大学信息管理学院情报学专业硕士研究生,研究方向为信息资源管理、信息分析、信息行为、信息系统。
郭佳,女,2026年生,武汉大学信息管理学院情报学专业硕士研究生,研究方向为信息资源管理、信息分析、信息行为、信息系统。
郭佳,女,2026年生,武汉大学信息管理学院情报学专业硕士研究生,研究方向为信息资源管理、信息分析、信息行为、信息系统。
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。







